Learning
System | Hardware
Motherboard |
CPU |
PSU |
RAM |
VGA |
NIC |
USB ports |
Sound Card |
UPS |
Scanner |
SerialPort |
VideoCamera |
TV tunner
1. Computer turns on for some time then it suddenly turns off.
2. Random black & blue screen crashes
3. Random Computer Crashes and Restarts.
4. Display Issues
5. Freezing
6. Smoke/Burning Smell
7. Strange noises from the PC case
8. Presence Of Frequent Electric Shocks When You Touch The Metallic Parts Of The Computer.
9. The power supply fan spins, but there is no power to other devices
10. PC won’t start, but the case fans spin.
11. Overheating of PSU
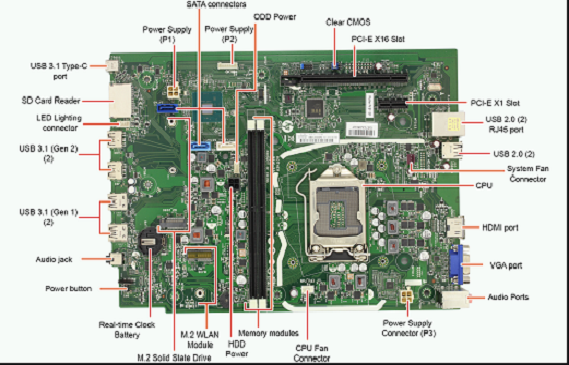
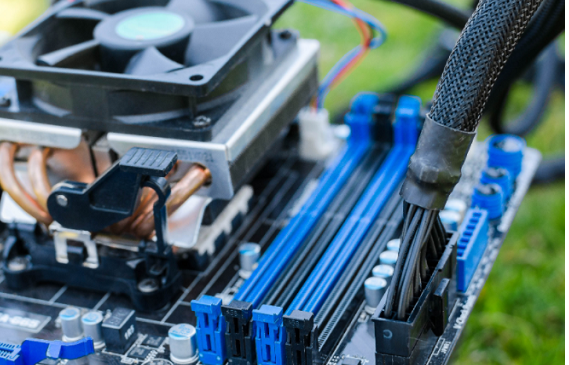
MotherBoard:
A motherboard is the main printed circuit board in general-purpose computers
and other expandable systems. It holds and allows communication between many
of the crucial electronic components of a system, such as the central processing
unit and memory, and provides connectors for other peripherals. Unlike a
backplane, a motherboard usually contains significant sub-systems, such as
the central processor, the chipset's input/output and memory controllers, interface
connectors, and other components integrated for general use.
- The computer may start to boot but then shuts down. Increased Windows errors or
"blue screens of death" are symptoms of failing motherboards. The computer may
freeze for seemingly no reason, or connected devices that worked before suddenly
won’t work.
-A very short beep is indicative of a problem with your motherboard. It can also mean
that you have a problem with your system memory (BIOS AWARD). -A long beep followed by three sequential short beeps signals an issue linked to
your graphics card configurations. -A short beep followed by three sequential long beeps means that you have a problem
with your system memory. -If you are hearing beep, pause, beep, pause, followed by two sequential beeps, the error
is linked to your CPU (central processing unit). -Three beeps, pause, three beeps, pause, followed by four beeps indicates an issue
with video memory. -One long beep and nine short beeps means there is a problem with the ROM (BIOS AWARD).
-Three beeps, pause, four beeps, pause, followed by a beep signals an error with
your graphics card. -Four beeps, pause, three beeps, pause, and then one beep indicates a system memory problem.
-Five short beeps is another indication of issues with your CPU.
-Long, constant beeps alert system memory problems.
A motherboard is the main printed circuit board in general-purpose computers
and other expandable systems. It holds and allows communication between many
of the crucial electronic components of a system, such as the central processing
unit and memory, and provides connectors for other peripherals. Unlike a
backplane, a motherboard usually contains significant sub-systems, such as
the central processor, the chipset's input/output and memory controllers, interface
connectors, and other components integrated for general use.
Some of the symptoms to look for when diagnosing a bad motherboard are failure to boot
- The computer may start to boot but then shuts down. Increased Windows errors or
"blue screens of death" are symptoms of failing motherboards. The computer may
freeze for seemingly no reason, or connected devices that worked before suddenly
won’t work.
-A very short beep is indicative of a problem with your motherboard. It can also mean
that you have a problem with your system memory (BIOS AWARD). -A long beep followed by three sequential short beeps signals an issue linked to
your graphics card configurations. -A short beep followed by three sequential long beeps means that you have a problem
with your system memory. -If you are hearing beep, pause, beep, pause, followed by two sequential beeps, the error
is linked to your CPU (central processing unit). -Three beeps, pause, three beeps, pause, followed by four beeps indicates an issue
with video memory. -One long beep and nine short beeps means there is a problem with the ROM (BIOS AWARD).
-Three beeps, pause, four beeps, pause, followed by a beep signals an error with
your graphics card. -Four beeps, pause, three beeps, pause, and then one beep indicates a system memory problem.
-Five short beeps is another indication of issues with your CPU.
-Long, constant beeps alert system memory problems.
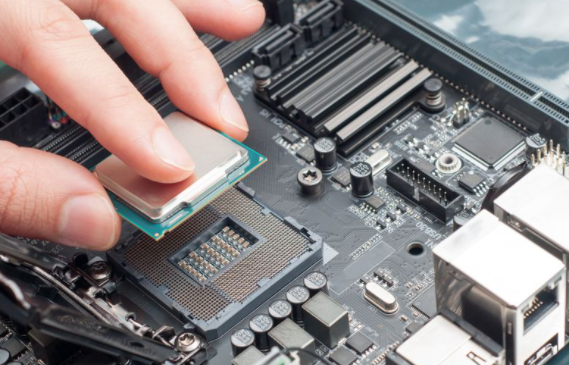
Central Processing Unit:
When you start the computer you won't hear any beep codes since the POST test is
not passed. The only thing you may hear is the fans running. Apart from that there
will be just a blank screen displayed. No matter how many times you press the keyboard
keys or click the mouse buttons you won't be able to get any response from the PC.
You can further confirm this by looking at the motherboard LED's. If the LED's happens
to light up when you turn on the PC but the system doesn't pass the POST test, it is
an indication of a processor failure.
CPUs generate more heat which is dispelled by the fans. If the fans get clogged with
dust and other particles, it will not be able to expel this excess heat out. As a
result the processor can get overheated to the maximum level that is not bearable. So
for preventing further damages to the processor the motherboard takes necessary actions
to shutdown the PC.
the PC components are functioning properly. If this test happens to encounter any problems
in the CPU it will indicate through a series of beep tones. Through the number of beeps you
can identify whether the problem is related with the processor. Usually the beeps are given
5-7 times if there are any issues with the CPU.
is exposed for heat for a long time it can get damaged permanently. Besides that there can be
charred marks left over on the CPU. You may also notice burn marks around the CPU socket.
In this type of cases the damages are more severe and irreversible. The only thing you can
do about it is simply replace them.
Booting Issues:
In the event of a CPU failure, it won't go through the normal process of booting.When you start the computer you won't hear any beep codes since the POST test is
not passed. The only thing you may hear is the fans running. Apart from that there
will be just a blank screen displayed. No matter how many times you press the keyboard
keys or click the mouse buttons you won't be able to get any response from the PC.
You can further confirm this by looking at the motherboard LED's. If the LED's happens
to light up when you turn on the PC but the system doesn't pass the POST test, it is
an indication of a processor failure.
Frequent Shutdowns:
A Processor that is more subjected to heat is more likely to undergo failure. In natureCPUs generate more heat which is dispelled by the fans. If the fans get clogged with
dust and other particles, it will not be able to expel this excess heat out. As a
result the processor can get overheated to the maximum level that is not bearable. So
for preventing further damages to the processor the motherboard takes necessary actions
to shutdown the PC.
Beeping Noises:
Every computer at its startup runs a self test known as POST. This test verifies if allthe PC components are functioning properly. If this test happens to encounter any problems
in the CPU it will indicate through a series of beep tones. Through the number of beeps you
can identify whether the problem is related with the processor. Usually the beeps are given
5-7 times if there are any issues with the CPU.
Physical Damages:
Generally a bad CPU can be identified through its external appearance. If the processoris exposed for heat for a long time it can get damaged permanently. Besides that there can be
charred marks left over on the CPU. You may also notice burn marks around the CPU socket.
In this type of cases the damages are more severe and irreversible. The only thing you can
do about it is simply replace them.
Power Supply:
1. Computer turns on for some time then it suddenly turns off.
2. Random black & blue screen crashes
3. Random Computer Crashes and Restarts.
4. Display Issues
5. Freezing
6. Smoke/Burning Smell
7. Strange noises from the PC case
8. Presence Of Frequent Electric Shocks When You Touch The Metallic Parts Of The Computer.
9. The power supply fan spins, but there is no power to other devices
10. PC won’t start, but the case fans spin.
11. Overheating of PSU
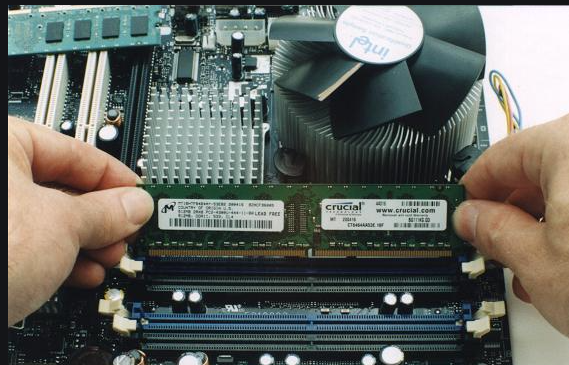
Random Access Memory:
computer and other expensive electronics into a surge protector. Make sure you know
the difference between a surge protector and a power strip.
-Before you handle any parts in your computer, make sure you ground yourself by touching
a piece of grounded metal to discharge static electricity. Electrostatic discharge
can damage your computer. -Excessive heat can cause RAM and other parts to wear out over time. Individual components
can overheat, or heat from one component can cause damage to adjacent parts. If you have overclocked any part of your computer incorrectly, it may cause damage in the
form of excess heat. Your memory module may have some fault that passed through quality control and worsened over
time. This is the most likely cause behind a damaged RAM.
What Causes Memory Damage?
-Power surges can damage most computer components, including RAM. You should plug yourcomputer and other expensive electronics into a surge protector. Make sure you know
the difference between a surge protector and a power strip.
-Before you handle any parts in your computer, make sure you ground yourself by touching
a piece of grounded metal to discharge static electricity. Electrostatic discharge
can damage your computer. -Excessive heat can cause RAM and other parts to wear out over time. Individual components
can overheat, or heat from one component can cause damage to adjacent parts. If you have overclocked any part of your computer incorrectly, it may cause damage in the
form of excess heat. Your memory module may have some fault that passed through quality control and worsened over
time. This is the most likely cause behind a damaged RAM.
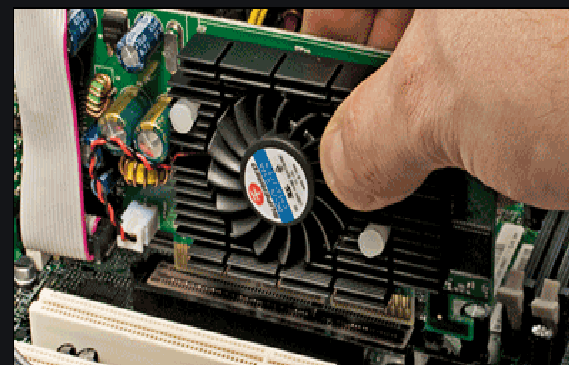
Video Graphic Adapter:
How To Know If Your Graphics Card Is Dying
1.1 Screen Turns Black
1.2 Crashes And Freezes
1.3 Blurred Text And Images
1.4 Suddenly Unable To Play Games
1.5 Missing Colors
1.6 Check For Bulges
1.7 Check For Discoloration
1.8 Check If Any Components Can Be Taken Off
1.9 Check If the Cable Is Missing Or Broken
1.10 Make Sure It’s Not
1.11 Check For Any Additional Slots
How To Know If Your Graphics Card Is Dying
1.1 Screen Turns Black
1.2 Crashes And Freezes
1.3 Blurred Text And Images
1.4 Suddenly Unable To Play Games
1.5 Missing Colors
1.6 Check For Bulges
1.7 Check For Discoloration
1.8 Check If Any Components Can Be Taken Off
1.9 Check If the Cable Is Missing Or Broken
1.10 Make Sure It’s Not
1.11 Check For Any Additional Slots
Network Interface Card:
One of the first things which should alert you to the imminent onset of NIC
issues is an intermittent network connection. If you notice your connection
keeps dropping out for periods of time – anything from a few seconds to hours
you probably have a NIC issue.
One of the first things which should alert you to the imminent onset of NIC
issues is an intermittent network connection. If you notice your connection
keeps dropping out for periods of time – anything from a few seconds to hours
you probably have a NIC issue.
Uninterruptible Power Supply:
is an electrical apparatus that provides emergency power to a load when the
input power source or mains power fails. A UPS differs from an auxiliary or
emergency power system or standby generator in that it will provide
near-instantaneous protection from input power interruptions, by supplying
energy stored in batteries, supercapacitors, or flywheels. The on-battery
run-time of most uninterruptible power sources is relatively short (only
a few minutes) but sufficient to start a standby power source or properly
shut down the protected equipment. It is a type of continual power system.
is an electrical apparatus that provides emergency power to a load when the
input power source or mains power fails. A UPS differs from an auxiliary or
emergency power system or standby generator in that it will provide
near-instantaneous protection from input power interruptions, by supplying
energy stored in batteries, supercapacitors, or flywheels. The on-battery
run-time of most uninterruptible power sources is relatively short (only
a few minutes) but sufficient to start a standby power source or properly
shut down the protected equipment. It is a type of continual power system.
SoundCard:
A sound card (also known as an audio card) is an internal expansion card
that provides input and output of audio signals to and from a computer under
the control of computer programs. The term sound card is also applied to
external audio interfaces used for professional audio applications.
A sound card (also known as an audio card) is an internal expansion card
that provides input and output of audio signals to and from a computer under
the control of computer programs. The term sound card is also applied to
external audio interfaces used for professional audio applications.
Universal Serial Bus:
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard that establishes specifications
for cables, connectors and protocols for connection, communication and power supply
(interfacing) between computers, peripherals and other computers.[2] A broad variety
of USB hardware exists, including 14 different connector types, of which USB-C is
the most recent and the only one not currently deprecated.
USB 1.0 = 12Mbps
USB 1.1 = 480Mbps
USB 2.0 = 480Mbps
USB 3.2 = 20Gbps
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard that establishes specifications
for cables, connectors and protocols for connection, communication and power supply
(interfacing) between computers, peripherals and other computers.[2] A broad variety
of USB hardware exists, including 14 different connector types, of which USB-C is
the most recent and the only one not currently deprecated.
USB 1.0 = 12Mbps
USB 1.1 = 480Mbps
USB 2.0 = 480Mbps
USB 3.2 = 20Gbps
Hand Held or FlatBed Scanner:
an electronic device that performs the same tasks as that of a flatbed scanner.
It is used to scan physical documents into their digital forms that can be
stored, edited, transferred and emailed digitally.
an electronic device that performs the same tasks as that of a flatbed scanner.
It is used to scan physical documents into their digital forms that can be
stored, edited, transferred and emailed digitally.
Serial Port or Com Port:
In computing, a serial port is a serial communication interface through which information
transfers in or out sequentially one bit at a time. This is in contrast to a parallel
port, which communicates multiple bits simultaneously in parallel.
In computing, a serial port is a serial communication interface through which information
transfers in or out sequentially one bit at a time. This is in contrast to a parallel
port, which communicates multiple bits simultaneously in parallel.
WebCAM:
A webcam is a small digital video camera that connects to a computer. It is also known
as a web camera that can capture pictures or motion video. These cameras come with
software that needs to be installed on the computer that helps transmit its video
on the Internet in real-time. It has the ability to take pictures, including HD
videos, but its video quality can be lower as compared to other camera models.
A webcam is a small digital video camera that connects to a computer. It is also known
as a web camera that can capture pictures or motion video. These cameras come with
software that needs to be installed on the computer that helps transmit its video
on the Internet in real-time. It has the ability to take pictures, including HD
videos, but its video quality can be lower as compared to other camera models.
TV Tunner:
A TV tuner is a device that you attach to your computer that will convert video ready
for TV into a format that the computer can understand in order to let you manipulate
that video to suit your needs. There are internal TV tuner cards that can perform
this function, but this is not always an option.
A TV tuner is a device that you attach to your computer that will convert video ready
for TV into a format that the computer can understand in order to let you manipulate
that video to suit your needs. There are internal TV tuner cards that can perform
this function, but this is not always an option.