Learning
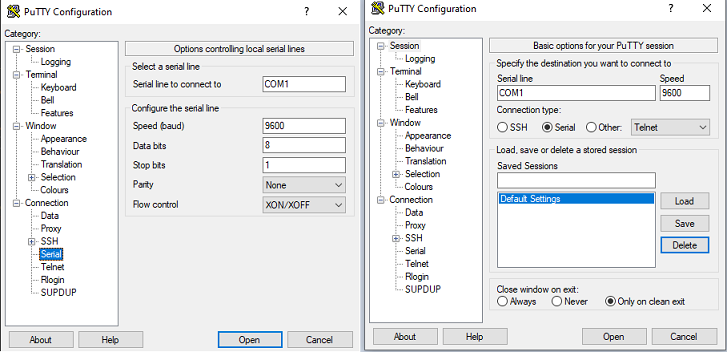
Putty_Serial

Putty_Telnet
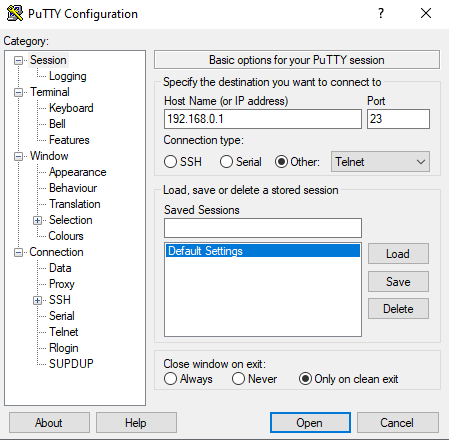

Putty_SSH
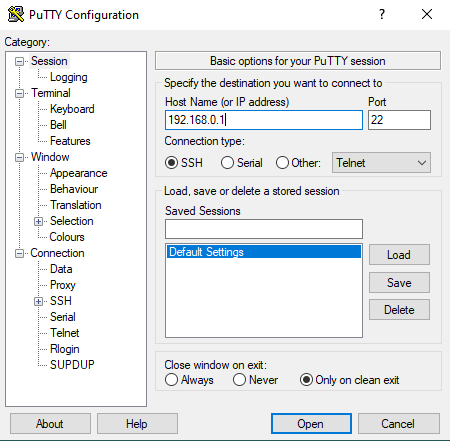

Telnet/SSH
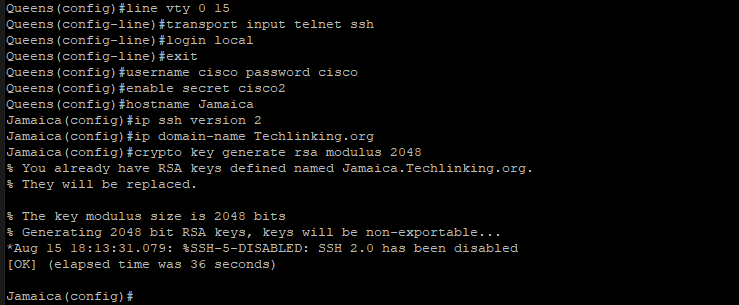

Secure Usermode with password
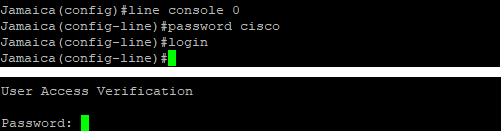

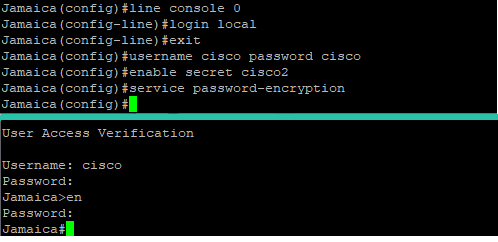
Full Console Security

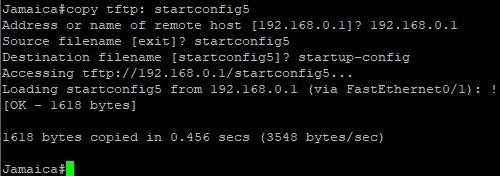
TFTP Flash


Copy startup-config to TFTP


Copy From TFTP to startup-config

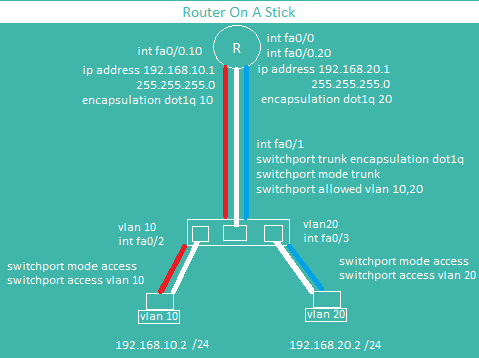
Inter Vlan Communication(ROAS)
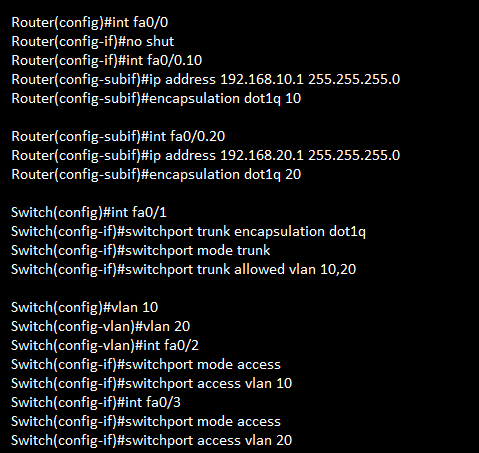
Inter Vlan | Inter Vlan IOS Configuration
Inter Vlan | Inter Vlan IOS Configuration
Inter VLAN

Inter VLAN IOS Configuration

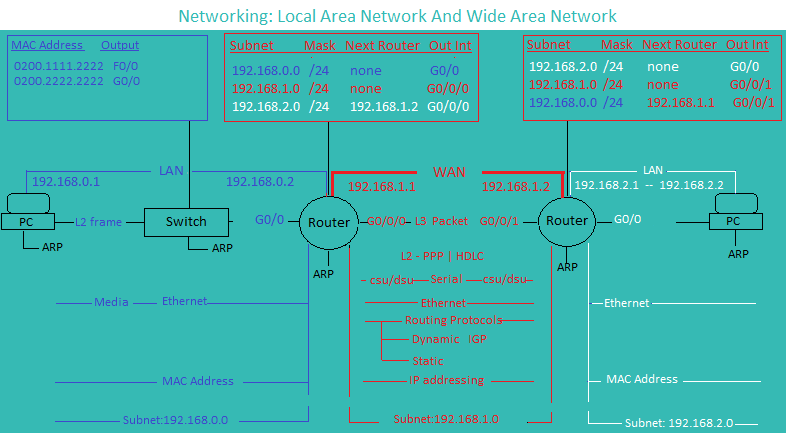
LAN/WAN Overview |
Net Config |
Routing Protocol
Network Overview
Network Overview
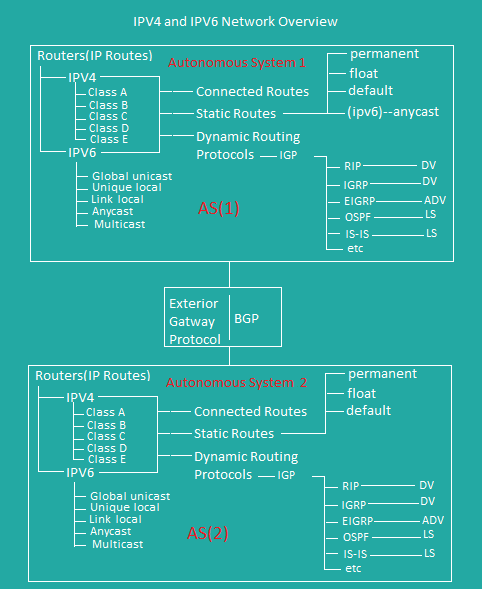

LAN/WAN

Interface
-
Interface Type:
-Internet | Serial | Cable TV | DSL | 3G/49 | More..... -
Interface configuration:
-Interface, Sub interface | IP address | Network mask | IP address dhcp | Duplex | Speed | More..... -
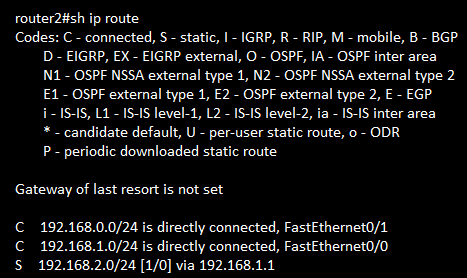
Static Routing:
-IP route | Host route | Default route | Floating | Decisions: Administrative Distance
-Longest route | Gateway of Last Resort ... -
Interior Gateway Protocol:
-Dynamic Routing: Rip, Ripv2, Ripng(ipv6), IGRP, EIGRP, IS-IS, OSPF ... -
Exterior Gateway Protocol:
-BGP autonomous | ....
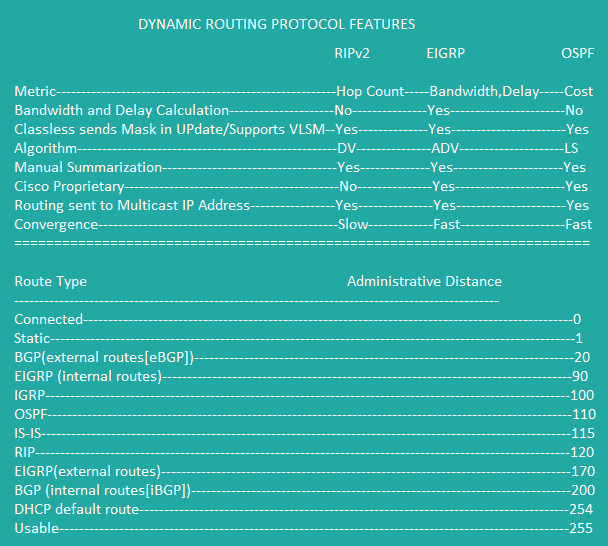
IGP: Metric
-
RIP Metric:
-Distance Vector
-hops or hop count : Hop count is the number of routers between a source
and destination: (up to 15). -
IGRP Metric:
-Distance Vector (DV) algorithm
-An intra-domain routing protocol
-Proprietary by Cisco
-Default[bandwidth, delay], load, reliability, and maximum transmission unit (MTU). -
EIGRP Metric: 256 * { K1*BW + [(K2*BW)/(256-load)] + (K3*delay) } * { K5/(reliability+K4) }
-Or 256 × ( Bandwidth + Delay )
-Distance vector & Link State routing protocol
-It uses DUAL that uses (diffusing update algorithm)
-It has five metrics: K1 = bandwidth, K2 = load, K3 = Delay, K4, K5 = reliability and MTU.
-EIGRP messages are Hello, Update, Query, Reply, and Acknowledgement.
-EIGRP uses a hello protocol to find neighboring routers
-Maintain a list of working neighbors
-Monitor ongoing hello messages to make sure the neighbor is still reachable
to notice when the path to a neighbor has failed.
-EIGRP exchange topology data which each router stores locally in a topology database.
-EIGRP uses topology database to describes facts about the network, but is a different
entity than the router’s IPv4 routing table. -
OSPF Metric:
-Link-state routing protocol
-Causes routers to learn routes.
-Choose the best route to each subnet based on a metric
-Converge to choose new best routes when the network changes.
-OSPF use a hello protocol to find neighboring routers
-Maintain a list of working neighbors
-Monitor ongoing hello messages to make sure the neighbor is still reachable
to notice when the path to a neighbor has failed.
-OSPF exchange topology data which each router stores locally in a topology database.
-OSPF uses topology database to describes facts about the network, but is a different entity
than the router’s IPv4 routing table.
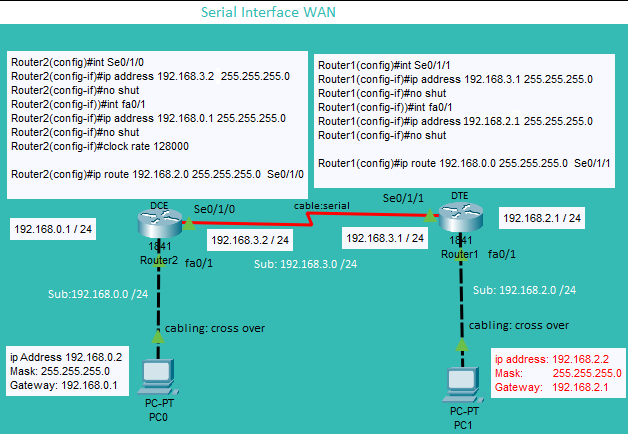
Serial
show ip interface brief | show ip interface interface-number | show ip route
Serial Interface Routing | IP Route Configuration | IP Route Configuration Continue
show ip interface brief | show ip interface interface-number | show ip route
Serial Interface Routing | IP Route Configuration | IP Route Configuration Continue
Serial Interface

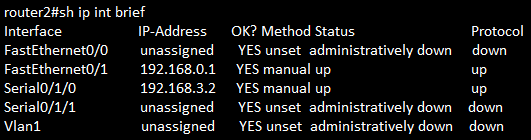
show ip interfaces brief

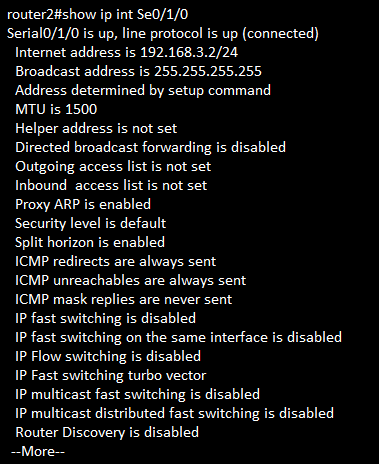
show ip interface interface-number

show ip route
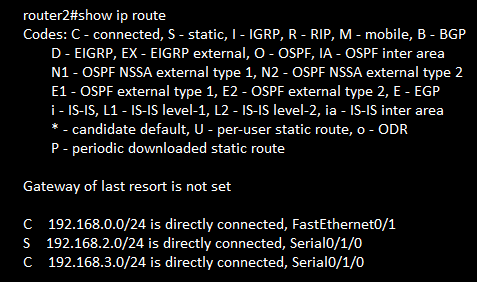

IPV4 Static, Float and Default Route
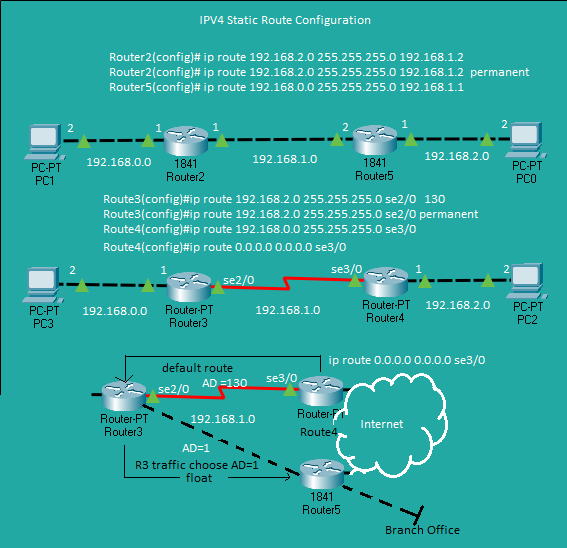

Ethernet
Ethernet WAN | IP Route Default and Float | show ip interface brief | show ip interface interface-number | show ip route
Ethernet WAN | IP Route Default and Float | show ip interface brief | show ip interface interface-number | show ip route
Ethernet WAN
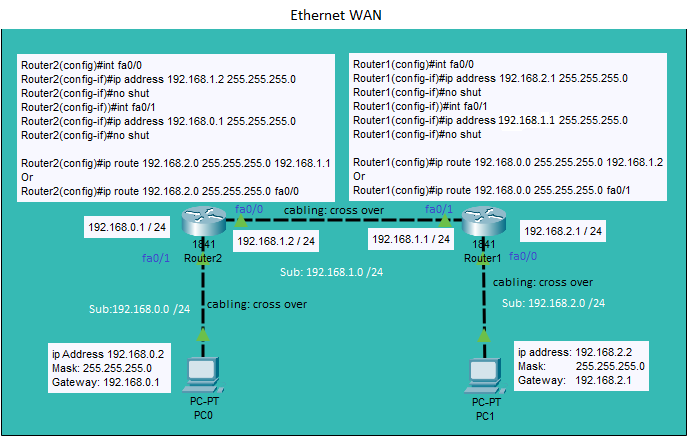

Ethernet IPV4 Static, Default and Float


show ip interfaces brief


show ip interface interface-number
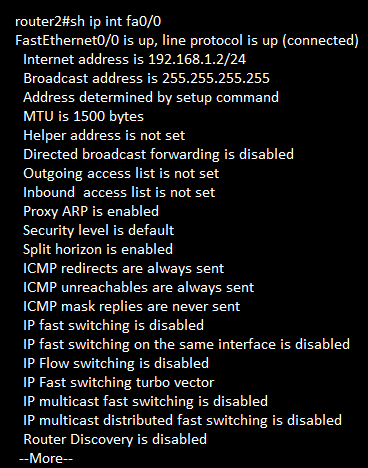

show ip route

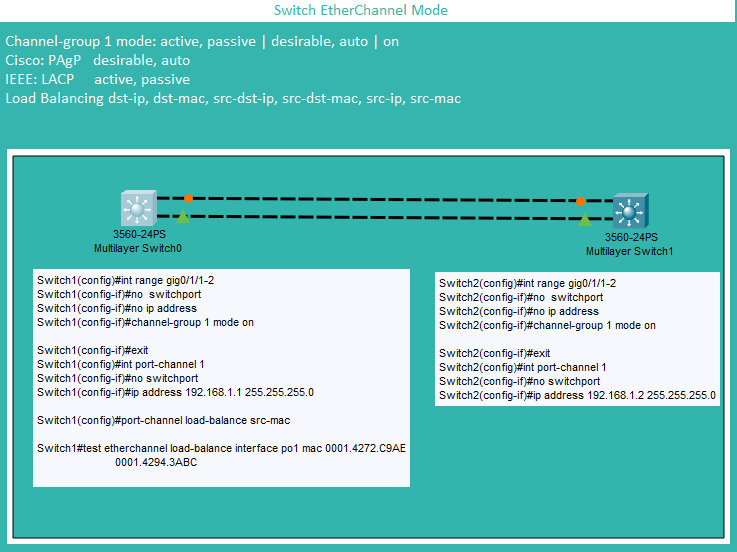
Ether Channel |
Layer 3 EtherChannel

Ipv4 Review
Classfull | Classful Key Facts | Classful Mask | Classful Info | Binary Conversion and Prefix Mask
Subnet And Broadcast Calculation | IPv4 Classfull And Classless A | IPv4 Classfull And Classless B
IPv4 Classfull And Classless C | Classless Example | IP Calculator
Classfull | Classful Key Facts | Classful Mask | Classful Info | Binary Conversion and Prefix Mask
Subnet And Broadcast Calculation | IPv4 Classfull And Classless A | IPv4 Classfull And Classless B
IPv4 Classfull And Classless C | Classless Example | IP Calculator
Classful
Classful
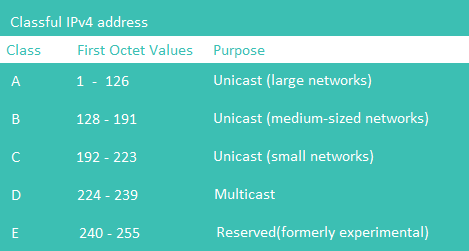

Classful Key Facts


Classful Mask
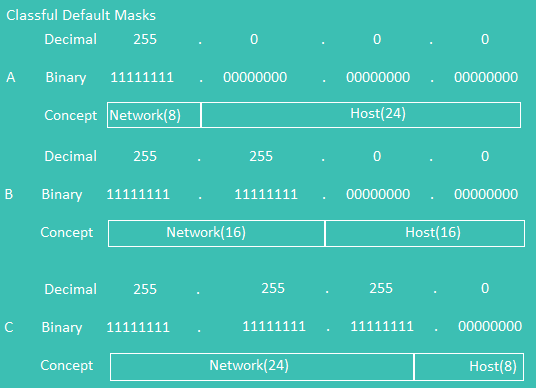

Classful Info


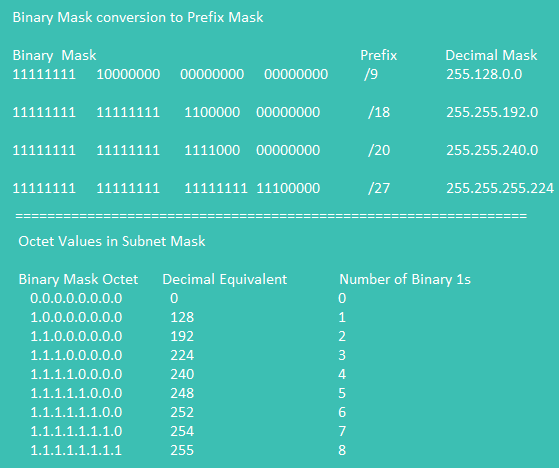
Binary Conversion And Prefix Mask

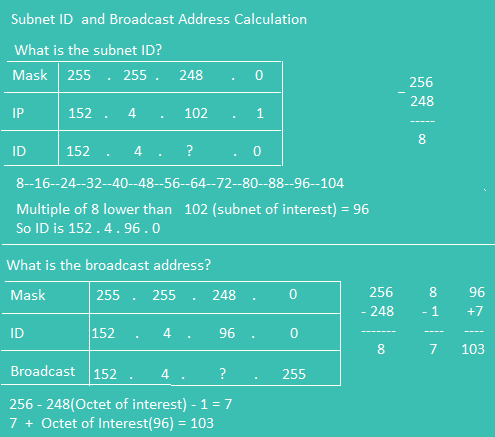
Subnet And Broadcast Calculation

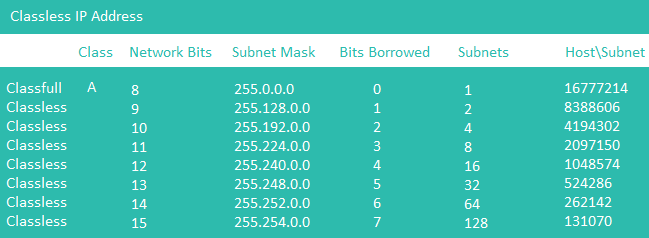
Class A of IPv4

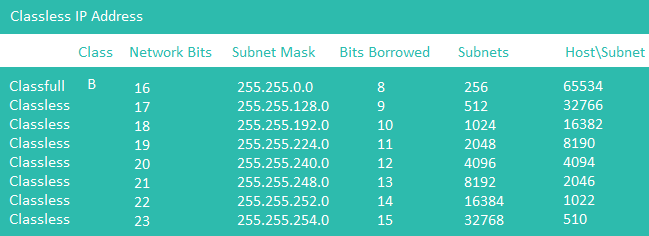
Class B of IPv4

Class C of IPv4
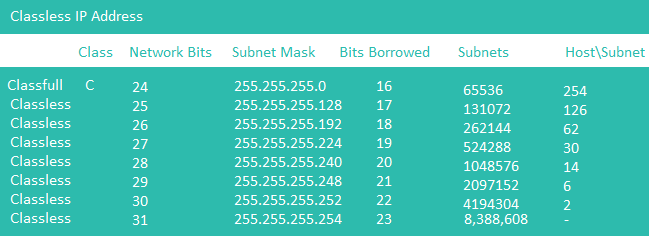

ClassLess C Example
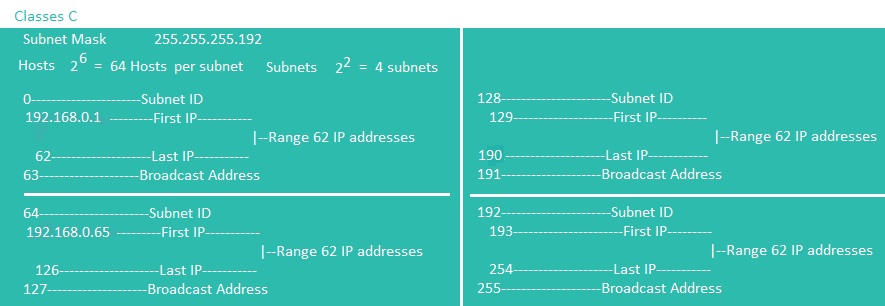

IPv6 Address And Subnetting
Abbreviation | IPv6 Subnetting | IPV6 Address | IPV6 Local Scope Multicast Addresses | IPv6 Multicast Scope Terms | More on IPv6 Multicast | IPV6 Command Reference | IPV6 More Command Reference | IPV6 Ethernet Configuration
IPV6 Serial Configuration | IPV6 Route Default and Float Schematic | IPV6 Route Default and Float Configuration | Show IPv6 Interface | Show IPv6 Interface Brief | Show IPv6 Route |

Abbreviation | IPv6 Subnetting | IPV6 Address | IPV6 Local Scope Multicast Addresses | IPv6 Multicast Scope Terms | More on IPv6 Multicast | IPV6 Command Reference | IPV6 More Command Reference | IPV6 Ethernet Configuration
IPV6 Serial Configuration | IPV6 Route Default and Float Schematic | IPV6 Route Default and Float Configuration | Show IPv6 Interface | Show IPv6 Interface Brief | Show IPv6 Route |
Abbreviation


IPv6 Subnetting
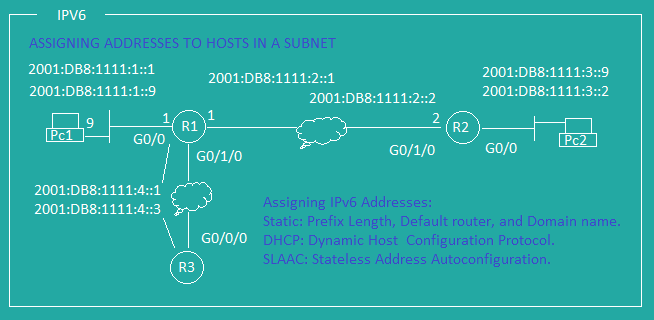

IPv6 Addresses


IPv6 Local-Scope Multicast Addresses


IPv6 Multicast Scope Terms


More on IPv6 Multicast


Command Reference


More Command Reference


IPv6 Serial Configuration


IPv6 Ethernet Configuration


IPv6 Route Default and Float Schematic


IPv6 Default and Float Configuration
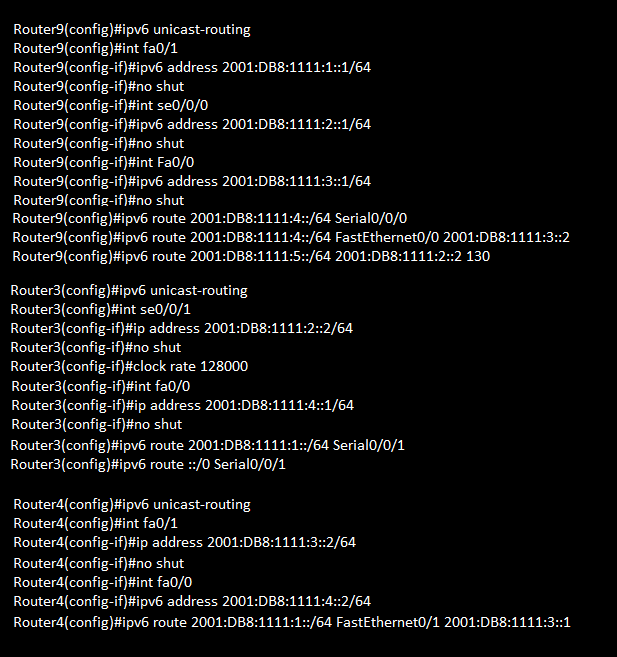

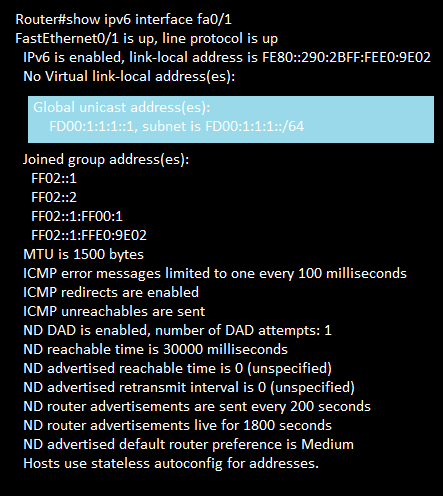
show ipv6 Interface

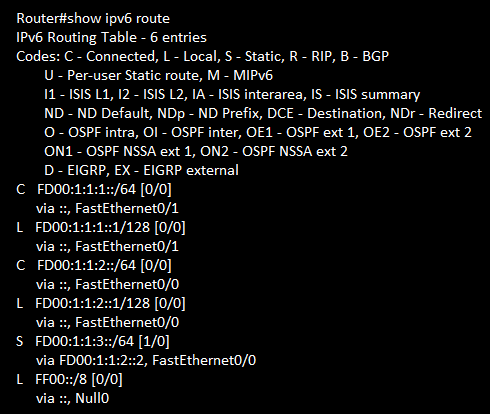
show ipv6 route


Ping |
Extended Ping |
Traceroute |
telnet and SSH
Trouble shooting problems
Trouble shooting problems
Extended Ping
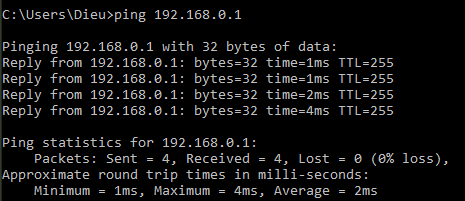
The ping command uses the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
ICMP echo request and ICMP echo reply messages for connectivity testing of Layer 3.
Ping the name or IP address of the destination
PC
Router
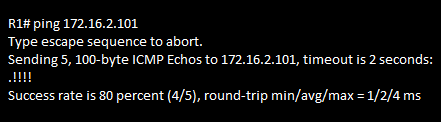
The ping command uses the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
ICMP echo request and ICMP echo reply messages for connectivity testing of Layer 3.
Ping the name or IP address of the destination
PC

Router

Extended Ping
Using Extended Ping to Test the Reverse Route
If a standard ping of a local LAN host works
But an extended ping of the same LAN host fails
The problem likely relates somehow to the host’s default router setting.
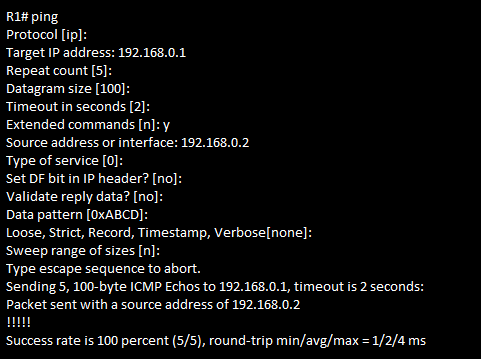
Using Extended Ping to Test the Reverse Route
If a standard ping of a local LAN host works
But an extended ping of the same LAN host fails
The problem likely relates somehow to the host’s default router setting.

TraceRoute
traceroute command systematically helps pinpoint routing problems by showing how far a
packet goes through an IP network before being discarded using ICMP Protocol TTL(Time To Live) message
Ex: Ethernet
PC1---192.168.0.2---192.168.0.1---R1---192.168.1.2------------192.168.1.1---R2---192.168.2.1-------192.168.2.2---PC2
PC:tracert
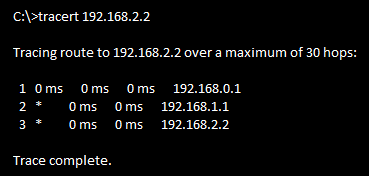
Router:traceroute
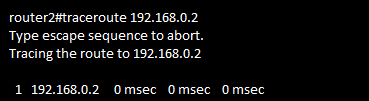
traceroute command systematically helps pinpoint routing problems by showing how far a
packet goes through an IP network before being discarded using ICMP Protocol TTL(Time To Live) message
Ex: Ethernet
PC1---192.168.0.2---192.168.0.1---R1---192.168.1.2------------192.168.1.1---R2---192.168.2.1-------192.168.2.2---PC2
PC:tracert

Router:traceroute

Telnet and SSH
Using the IOS Telnet client via the telnet host command
Router:Telnet

Router:SSH

Using the IOS Telnet client via the telnet host command
Router:Telnet

Router:SSH

Network Overview |
IGP Dynamic Routing Features |
OSPF Concept And Operation
More OSPF Concept And Operation | OSPF Network Type Broadcast | OSPF Network Type Point-To-Point | OSPF Network Types Configuration | OSPF Network ID Wildcard, Passive Interface, Default Route | OSPF Interface Cost Setting | OSPF Load Balancing | OSPF Command Reference1 | OSPF Command Reference2 | OSPF Command Reference3 | show ip ospf
show ip ospf int type_number | show ip ospf neighbor | show ip ospf database | show ip protocols | OSPF Multi Areas
More OSPF Concept And Operation | OSPF Network Type Broadcast | OSPF Network Type Point-To-Point | OSPF Network Types Configuration | OSPF Network ID Wildcard, Passive Interface, Default Route | OSPF Interface Cost Setting | OSPF Load Balancing | OSPF Command Reference1 | OSPF Command Reference2 | OSPF Command Reference3 | show ip ospf
show ip ospf int type_number | show ip ospf neighbor | show ip ospf database | show ip protocols | OSPF Multi Areas
Network Overview
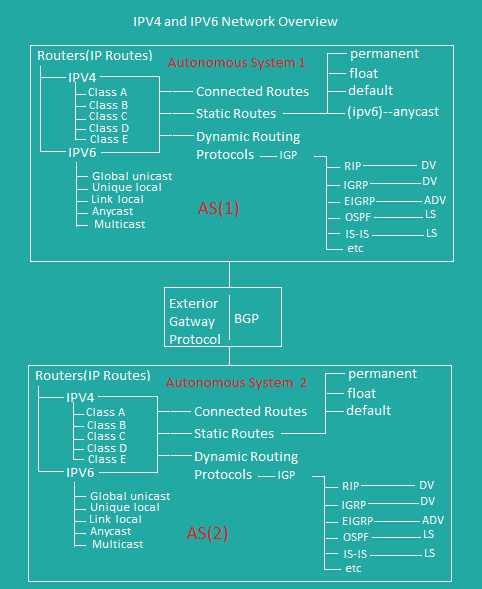

Dynamic Routing features

OSPF Concept and Operation
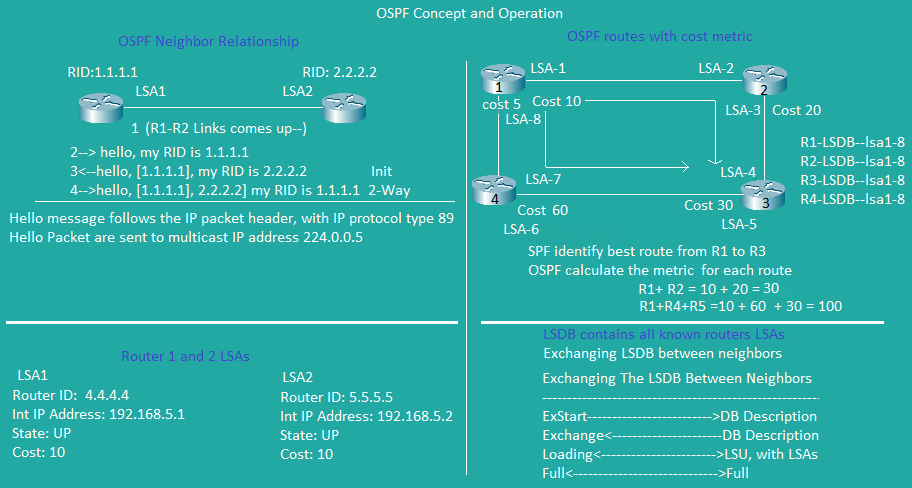

More OSPF Concept and Operation


OSPF Network Type Broadcast


OSPF Network Type Point-To-Point


OSPF Network Type Configuration


Network ID WildCard, Passive and Default Routes


OSPF Interface Cost Setting


OSPF Load Balancing


OSPF Command Reference 1


OSPF Command Reference 2
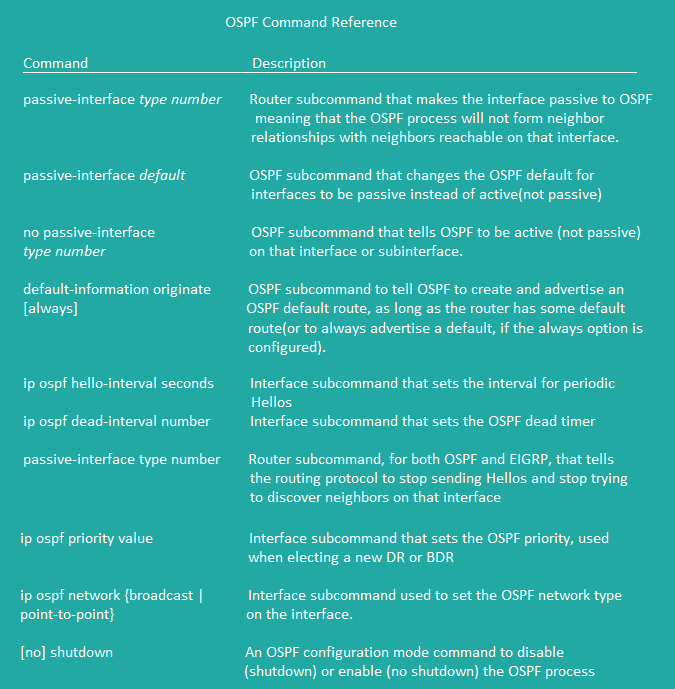

OSPF Command Reference 3


show ip ospf


show ip ospf type_number


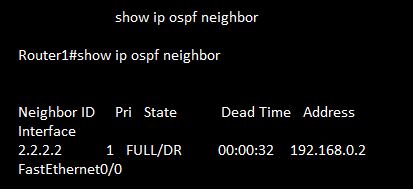
show ip ospf neighbor


show ip ospf database


show ip ospf protocols

OSPF Multi Areas


Wireless Access Point 1 |
Wireless Access Point 2 |
Wireless Access point 3 |
Wireless Cisco AP Terminology
Wireless Cisco Teminology | Wireless Cisco Architecture | Wireless Cisco WLC Activities
Wireless Cisco LAN Schematic | Wireless Cisco LAN Configuration | Wireless Security Terms
Wireless Security | Wireless Security Terminology | Wireless Security and Privacy | Wireless Security WPAs
Wireless Config Interface
Wireless Cisco Teminology | Wireless Cisco Architecture | Wireless Cisco WLC Activities
Wireless Cisco LAN Schematic | Wireless Cisco LAN Configuration | Wireless Security Terms
Wireless Security | Wireless Security Terminology | Wireless Security and Privacy | Wireless Security WPAs
Wireless Config Interface
Wireless Access Point 1


Wireless Access Point 2
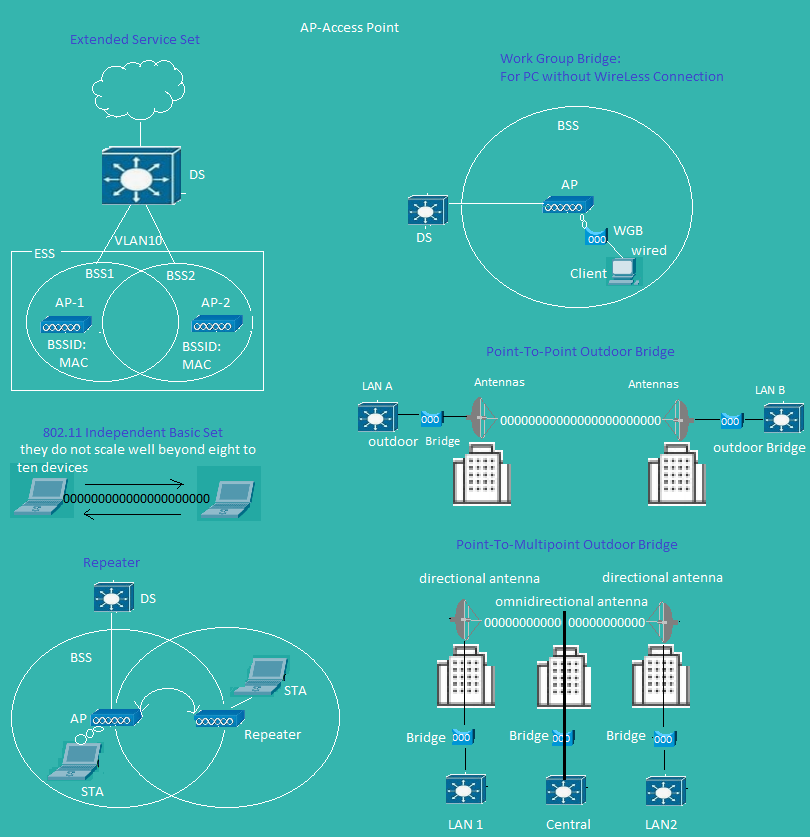

Wireless Access Point 3


Cisco Access Point Modes


Cisco Wireless Terminology


Cisco Wireless Architecture


Cisco WLC Activities


Cisco Wireless LAN Schematic
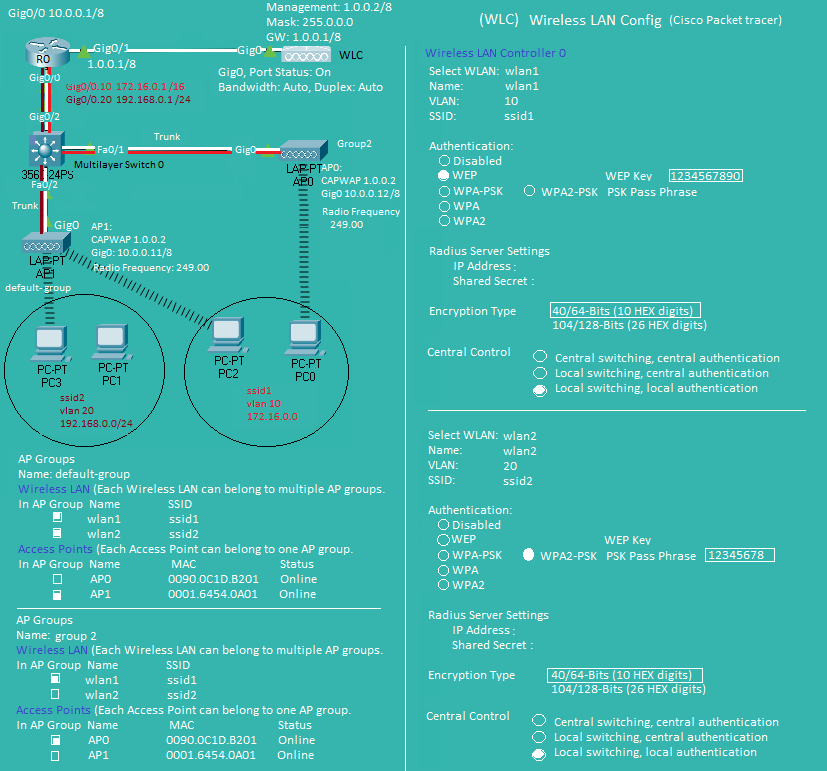

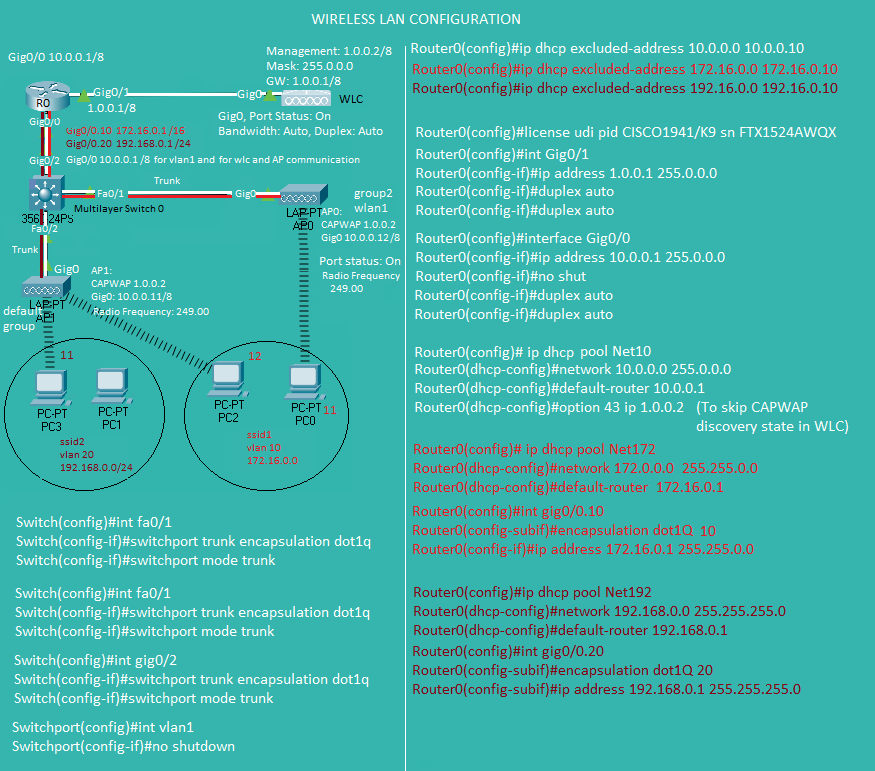
Cisco Wireless LAN Configuration

Wireless Security and Privacy Key Term


Wireless and Security
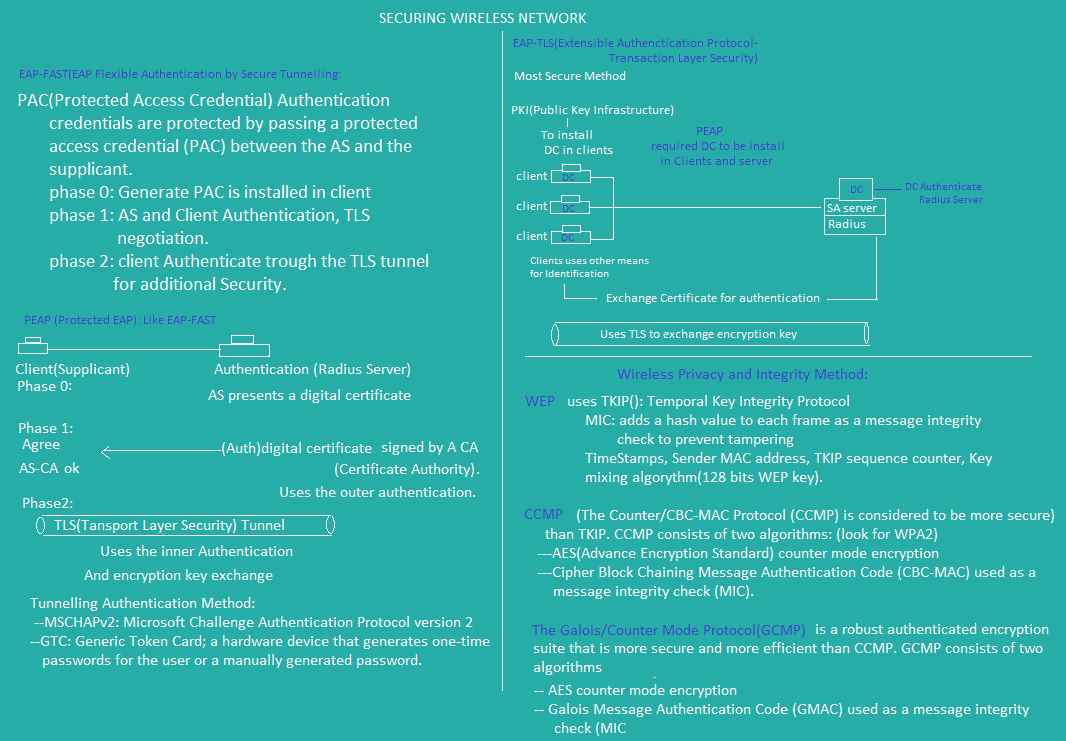

Wireless Terminology


Wireless and Security


Wireless Authentication [wpa,wpa2,wpa3]


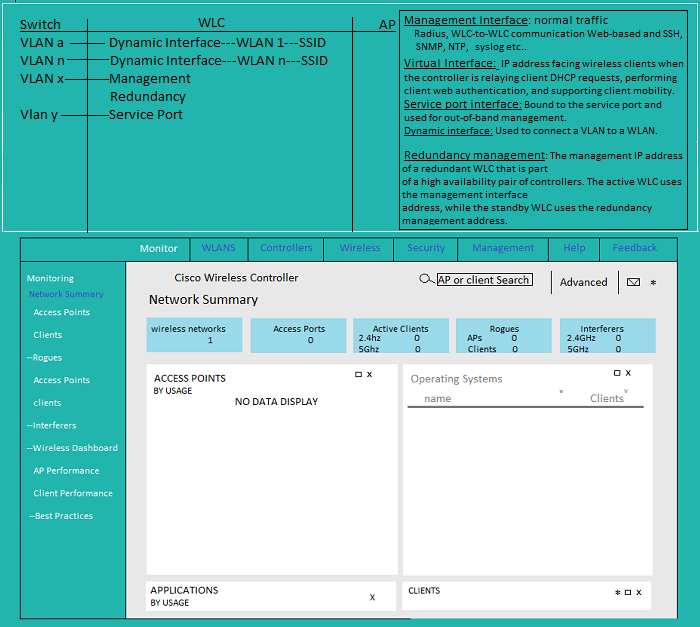
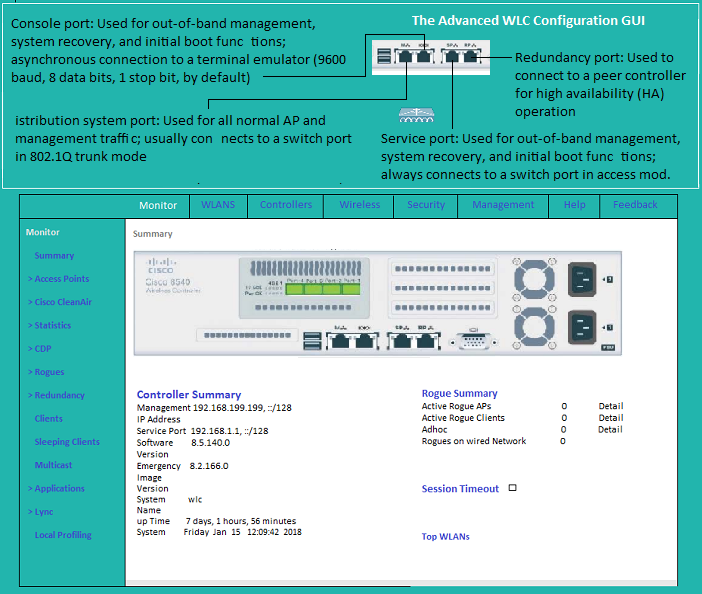
Wireless LAN Controller(WLC)
Monitor | WLANs | Controllers | Wireless | Security | Management | Help | Feedback

Monitor | WLANs | Controllers | Wireless | Security | Management | Help | Feedback
Wlan: List |
Wlan: New WLAN |
Wlan: General|
Wlan: Security L2 |
Wlan: Security AAA | Wlan: QOS | Wlan: Advanced
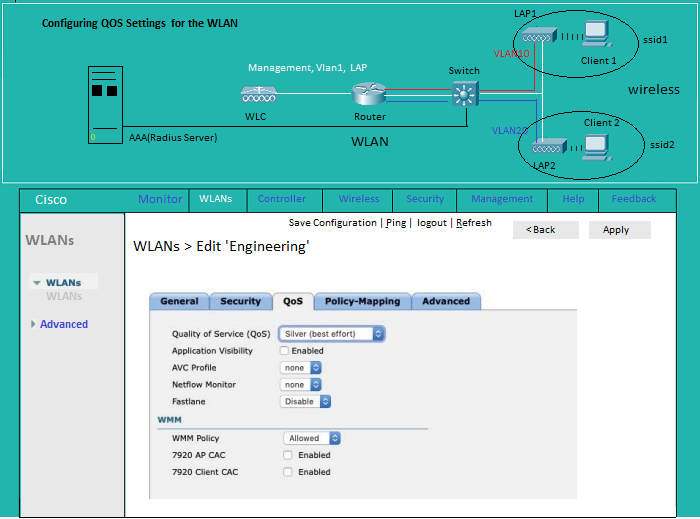

Wlan: Security AAA | Wlan: QOS | Wlan: Advanced
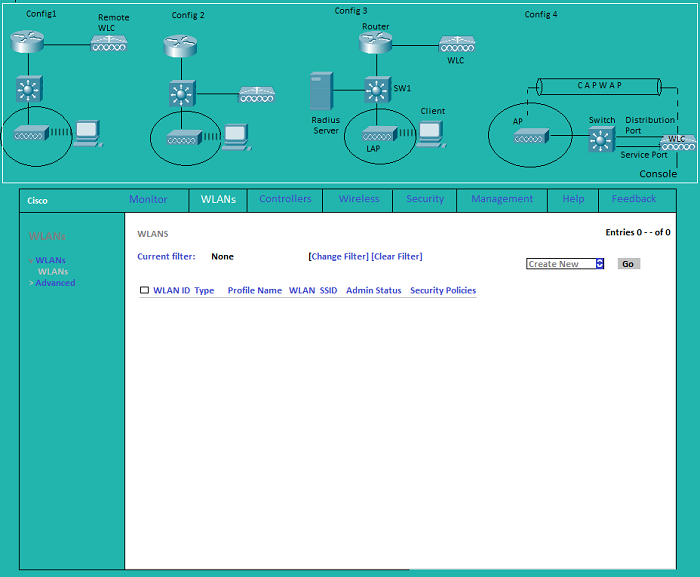
WLAN: Display a list of WLANs

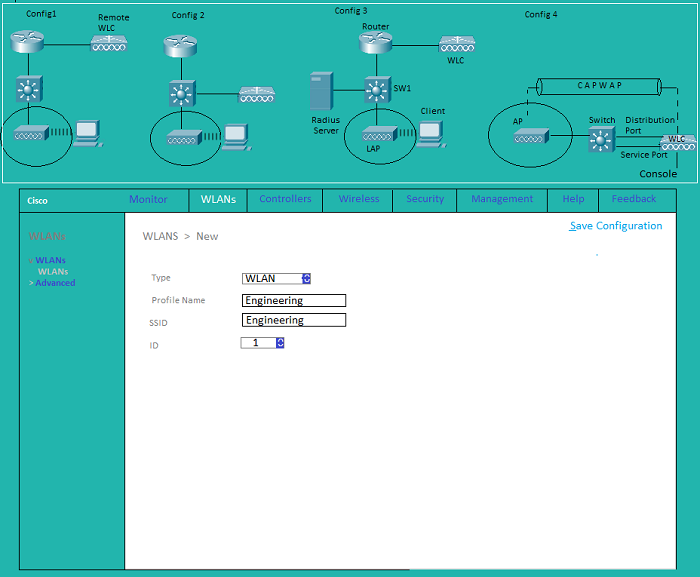
WLAN: Creating a new WLAN

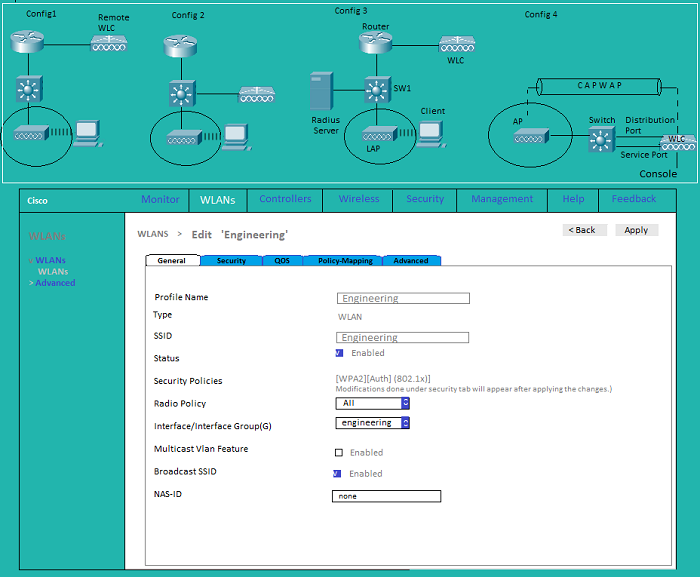
WLAN: General

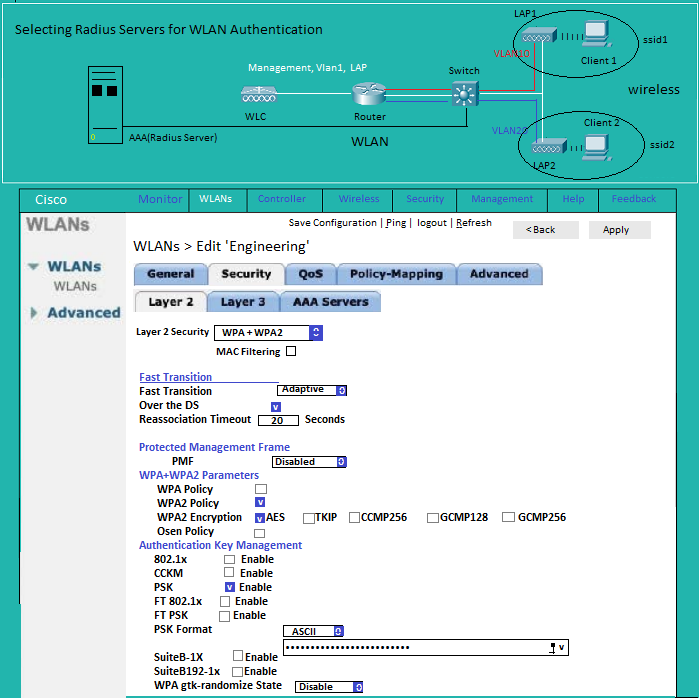
WLAN: Security L2

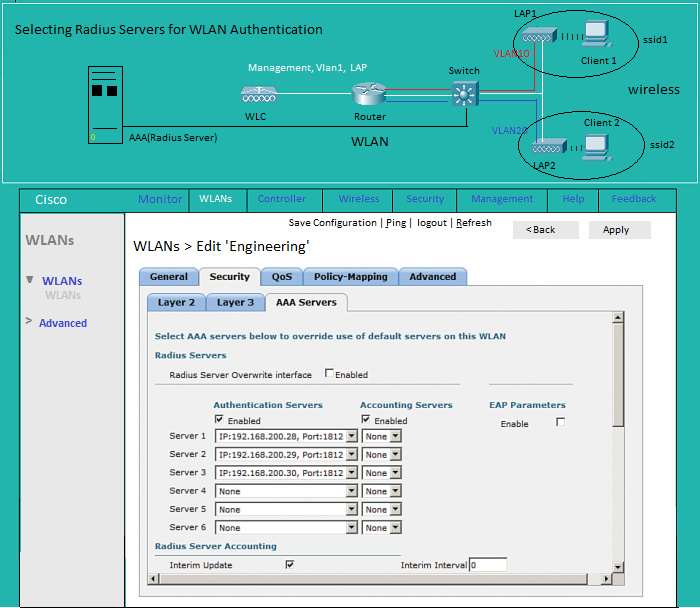
WLAN: Security AAA

WLAN: QoS

WLAN: Advanced

Controllers
Wlan: Displaying(D.I.) | Wlan: Defining(D.I.) | Wlan: Editing(D.I.)Controller: List of Dynamic Interfaces

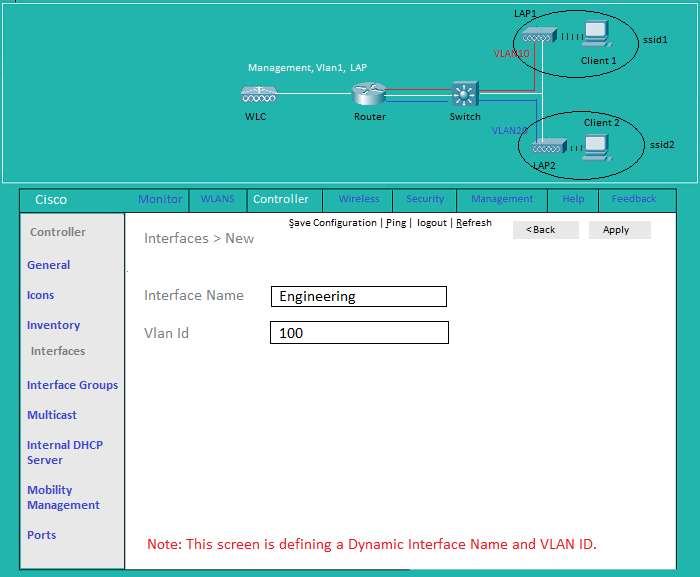
Controller: Defining Dynamic Interface Name and Vlan ID

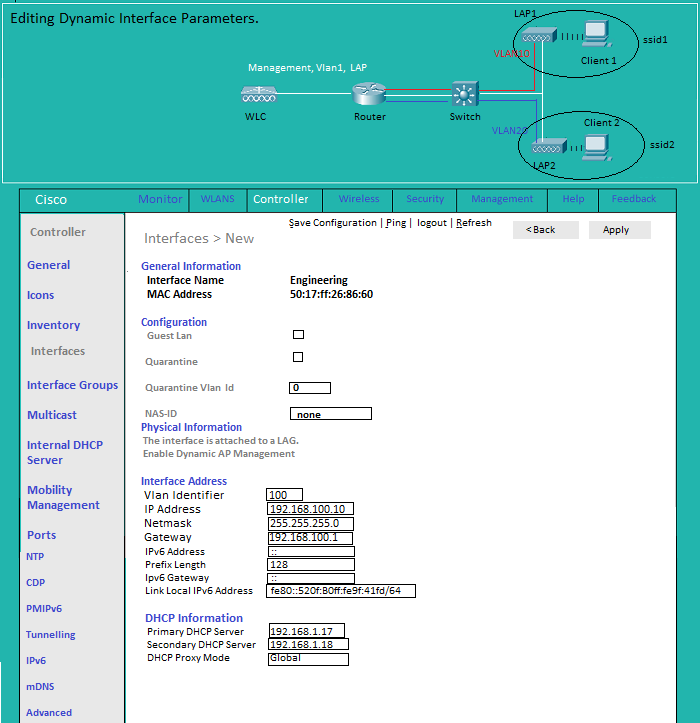
Controller: Editing Dynamic Interface Parameters

List of Radius(Aut Serv) |
Configuring Radius(Serv)
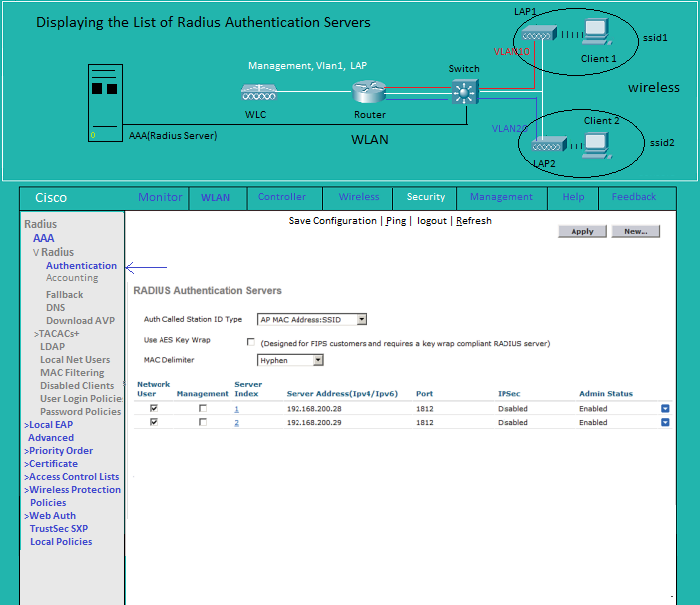

Security:List of Radius Authentication Servers

Security:Configuring a new Radius Server

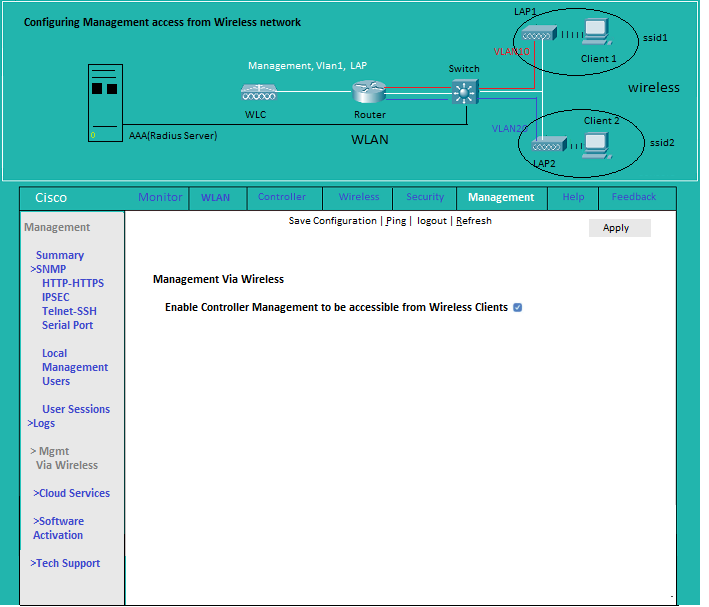
Management Access to from Wireless Networks

Help
Feedback
1_TCP Transport Layer(4) |
2_TCP Transport Layer(4) |
Standard ACL Commands |
Standard ACL Standard
Standard ACL Show Commands |
Standard ACL Show Commands |
Standard ACL Transport 1
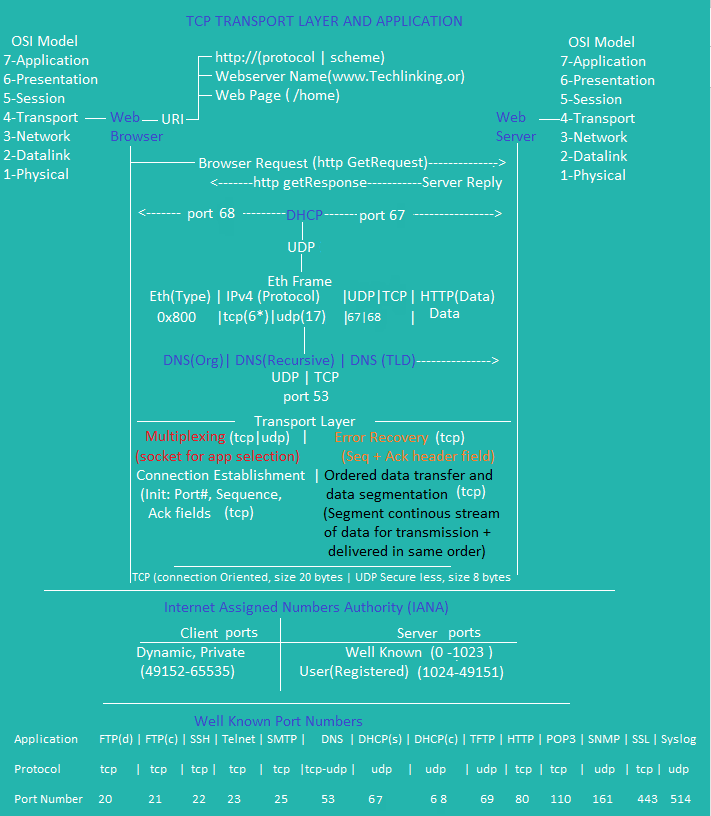

Standard ACL Transport 2
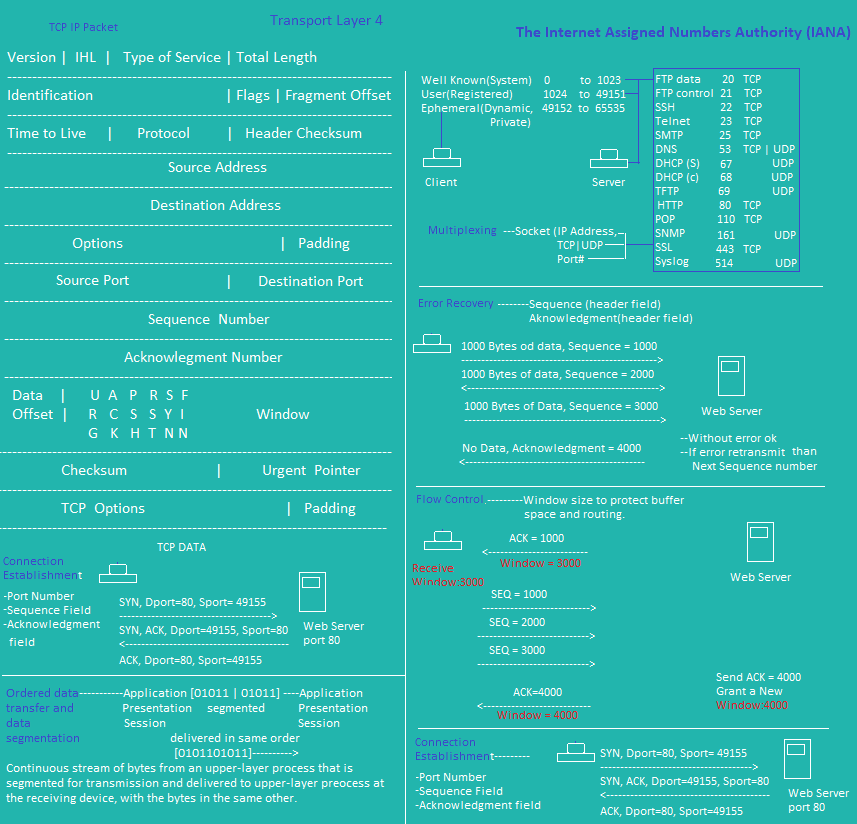

Standard ACL Commands


Standard ACL
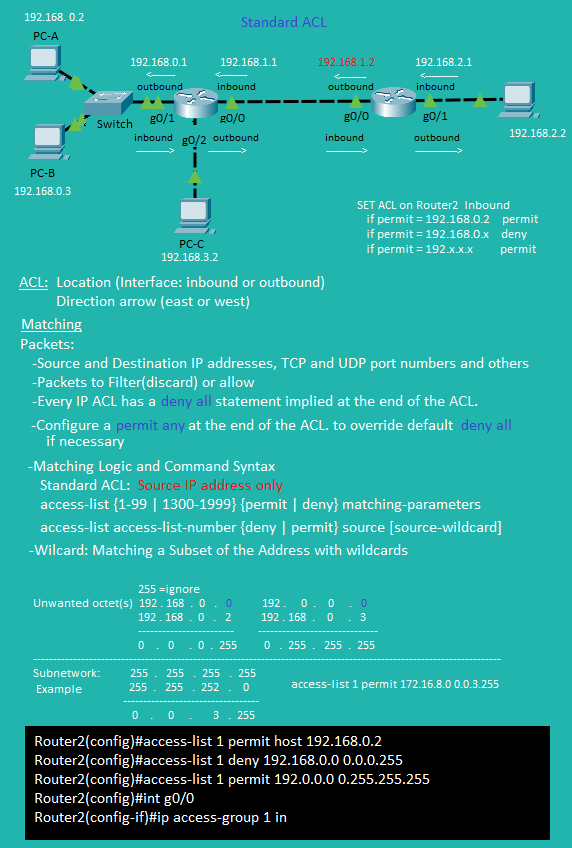

Standard ACL Show Commands
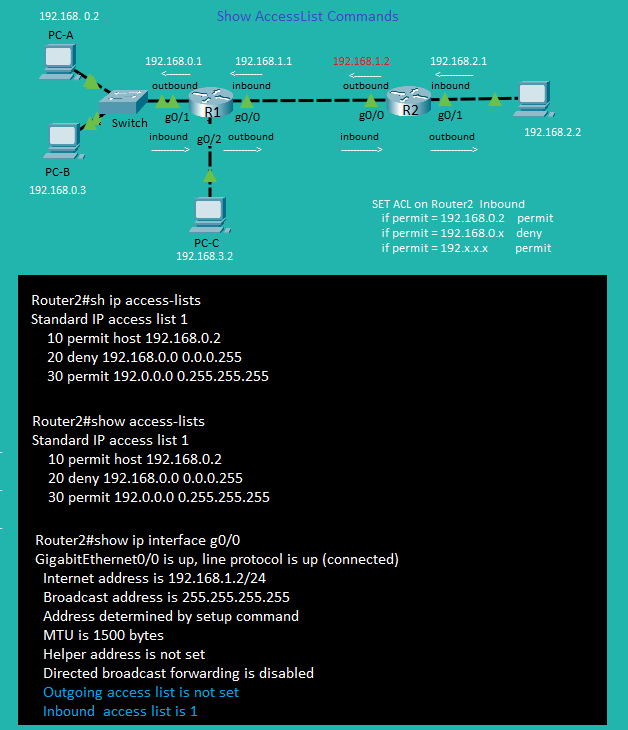

Standard ACL Practice


Extended ACL Theory 1 |
Extended ACL Theory 2 |
Extended ACL Numbered vs Named
Extended ACL Example 1 | Standard ACL Example 2 | Extended ACL Commands
Extended ACL Example 1 | Standard ACL Example 2 | Extended ACL Commands
Extended ACL Theory 1
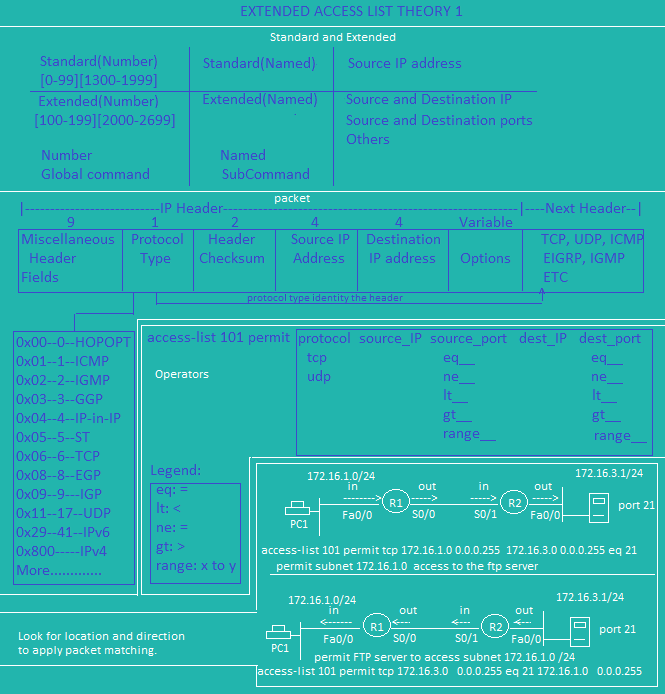

Extended ACL Theory 2


Extended ACL Number and Name


Extended ACL Example 1
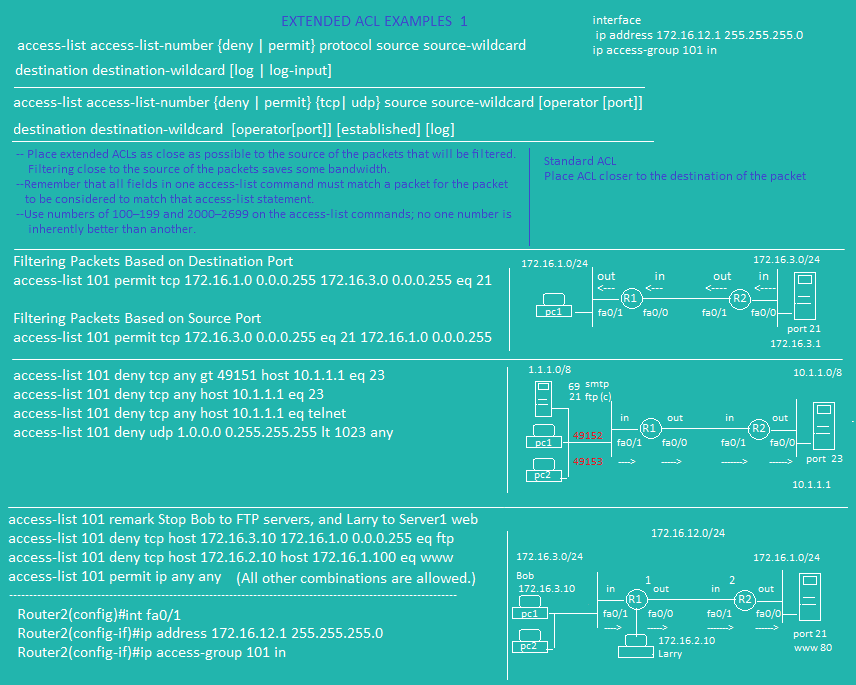

Extended ACL Example 2


Extended ACL Commands


Security Terminology 1 |
Security Terminology 2 |
Security Terminology 3 |
Security Terminology 4 |
Security Terminology 1


Security Terminology 2
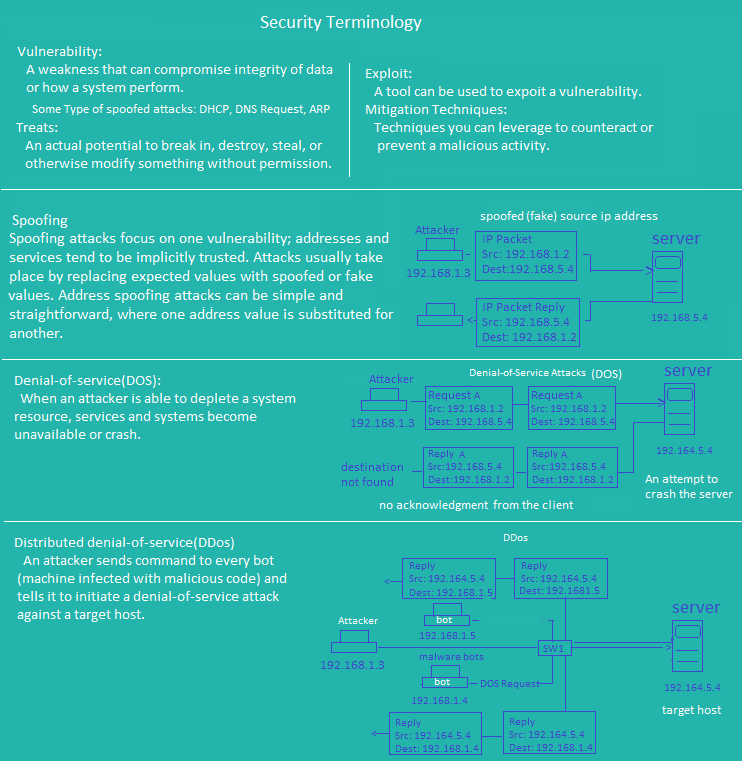

Security Terminology 3
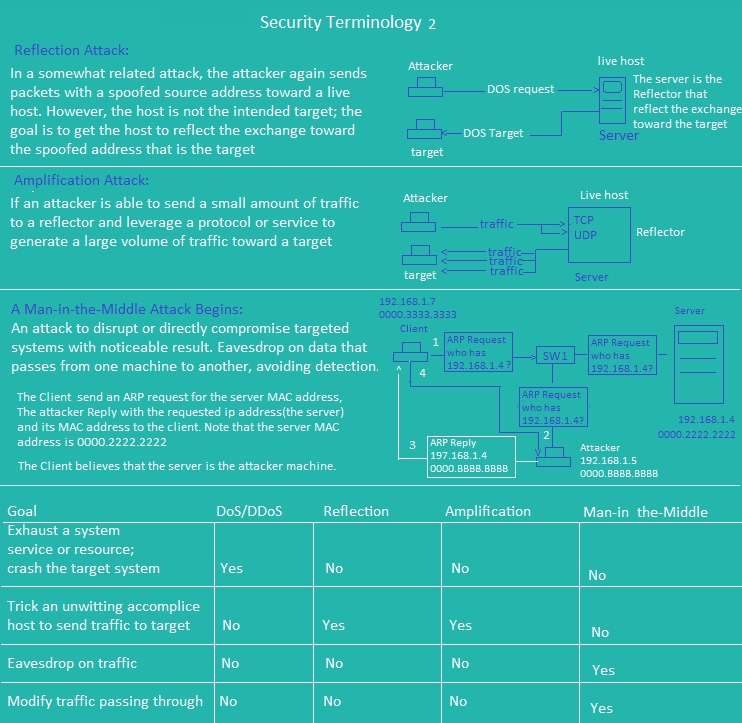

Security Terminology 4


Security Terminology 5


NAT Terminology |
NAT Static |
NAT Dynamic |
NAT Overload 1 |
NAT Overload 2
Network Address Translation Terminology


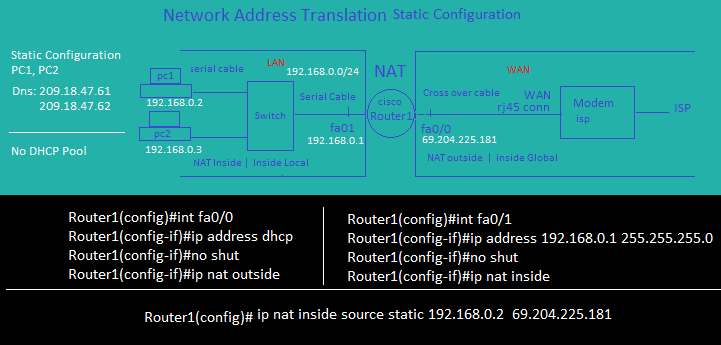
Network Address Translation Static

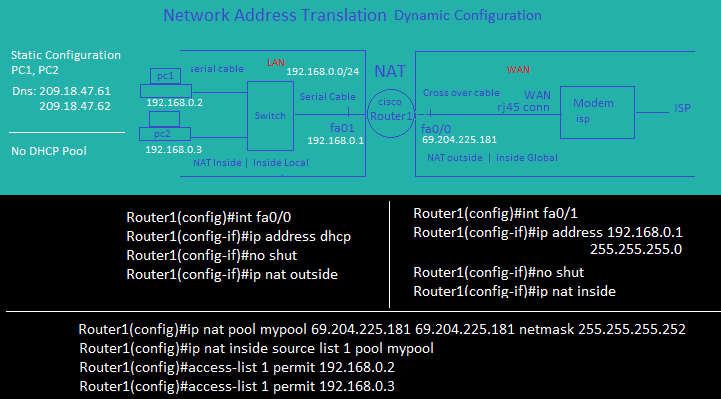
Network Address Translation Dynamic

Network Address Translation Overload 1


Network Address Translation Overload 2
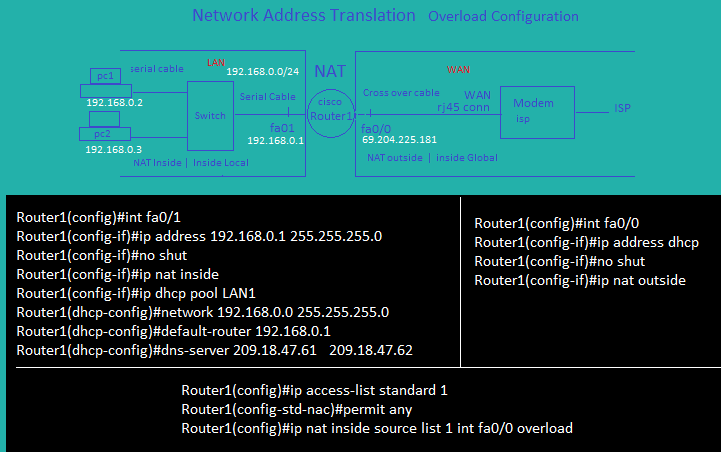

MPLS |
MPLS-L2VPN |
EoMPLS |
MPLS-L3VPN |
MPLS-Command |
MPLS-Show Command
MPLS_Terminology


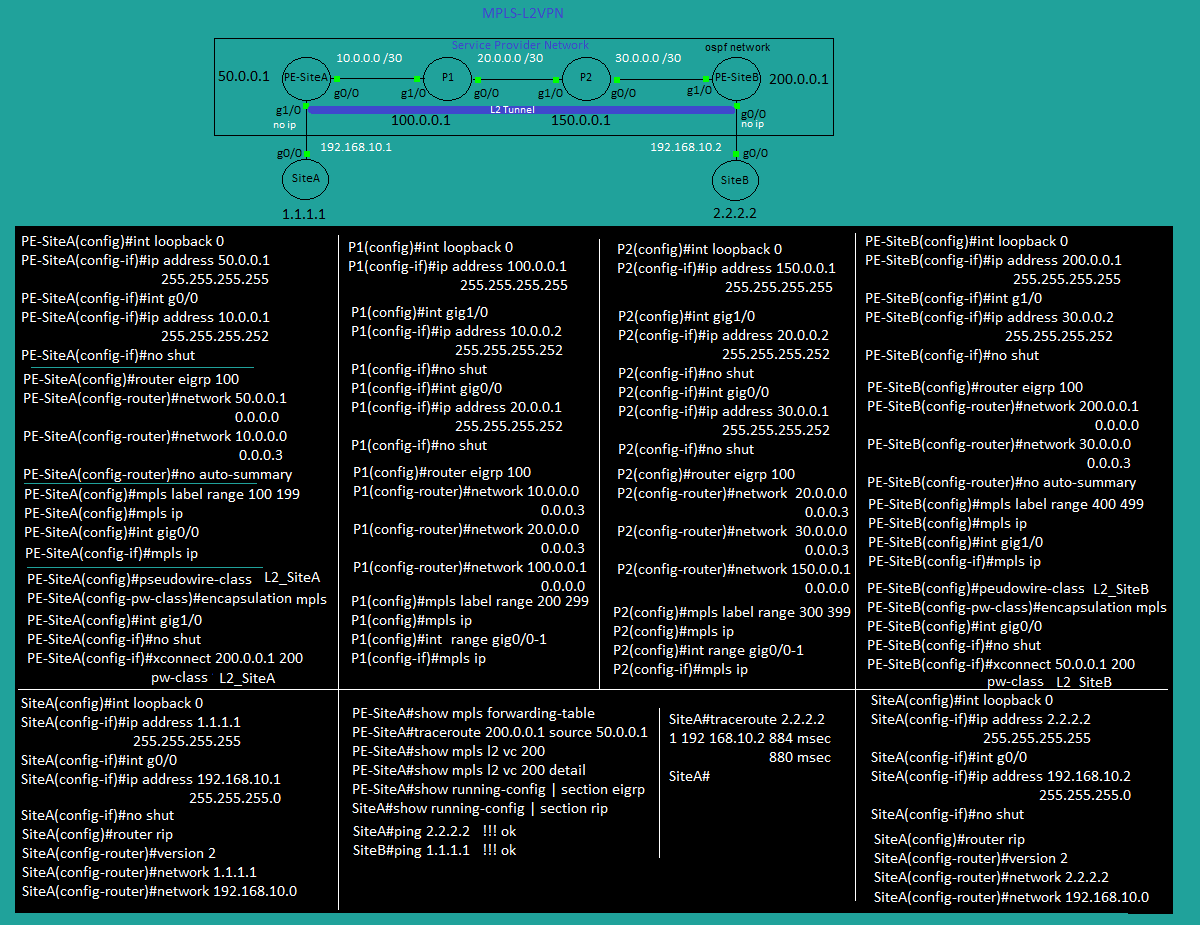
Multi Protocol Label Switching Layer 2 Virtual Private Network (MPLS_L2vpn)

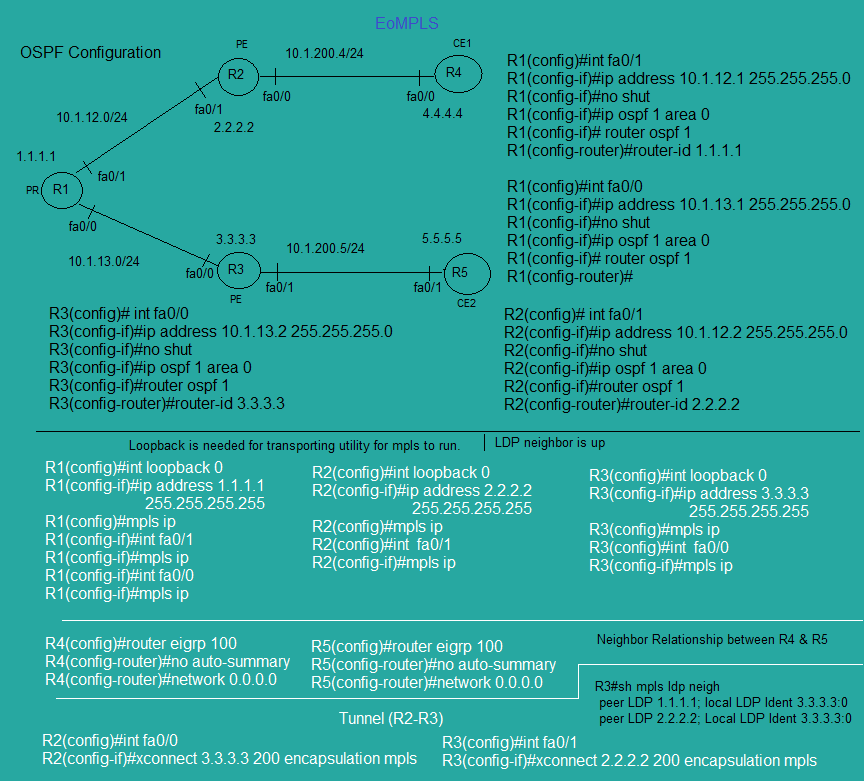
Multi Protocol Label Switching Layer 2 Virtual Private Network (EoMPLS)

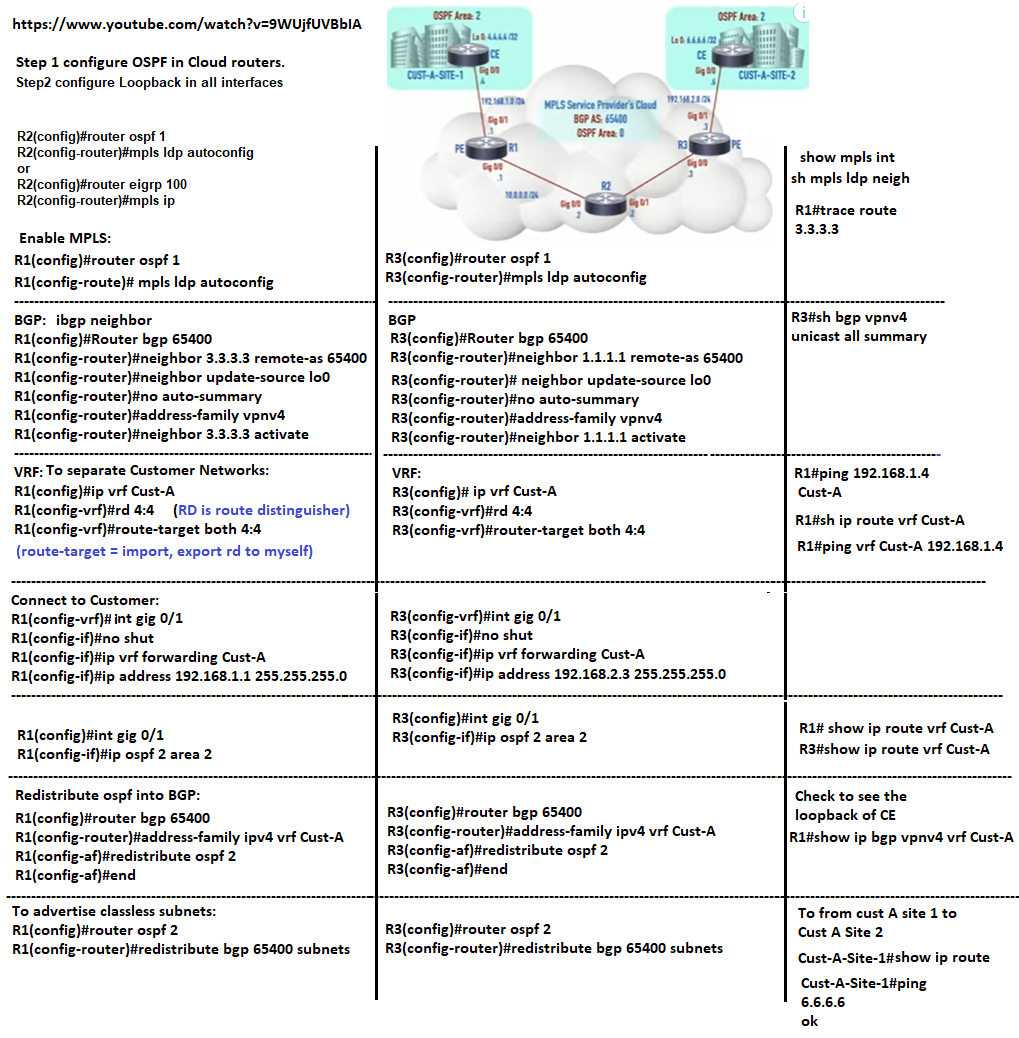
Multi Protocol Label Switching Layer 3 Virtual Private Network (MPLS_L3vpn)

MPLS Command


MPLS Show Command


SDN |
SDN-Terminology1 |
SDN-Terminology2 |
SDN-Terminology3 |
SDN-Terminology4 |
SDN-Terminology5 |
SDN-Terminology6
SDN-Terminology7 | SDN-Terminology8 | SDN-Terminology9 | SDN-Terminology10 | SDN-Terminology11 | SDN-Terminology12
SDN-Terminology13 | SDN-Terminology14 | SDN-Terminology15 | SDN-Terminology16 | SDN-Terminology17 | SDN-Terminology18
SDN-Terminology19 | SDN-Terminology20 | SDN-Terminology21 |
SDN-Terminology7 | SDN-Terminology8 | SDN-Terminology9 | SDN-Terminology10 | SDN-Terminology11 | SDN-Terminology12
SDN-Terminology13 | SDN-Terminology14 | SDN-Terminology15 | SDN-Terminology16 | SDN-Terminology17 | SDN-Terminology18
SDN-Terminology19 | SDN-Terminology20 | SDN-Terminology21 |
sdn_term


sdn_topology


sdn_topology2


sdn_topology3
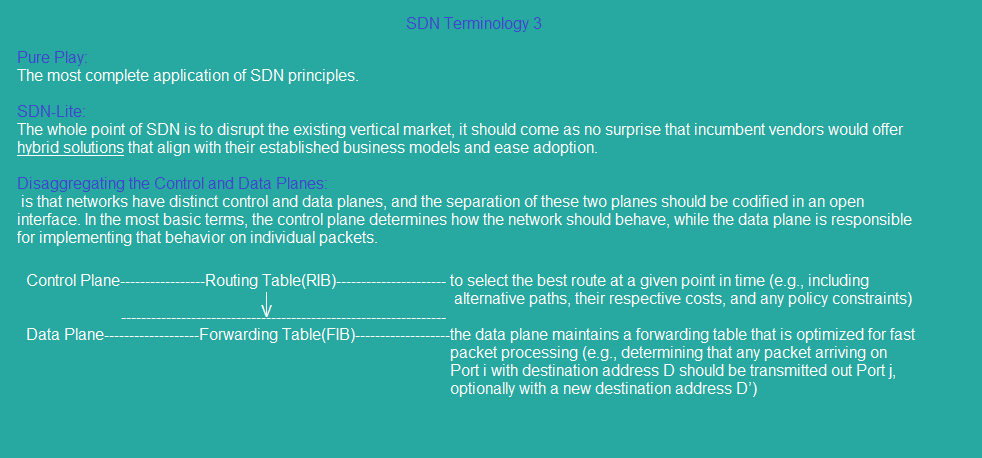

sdn_topology4
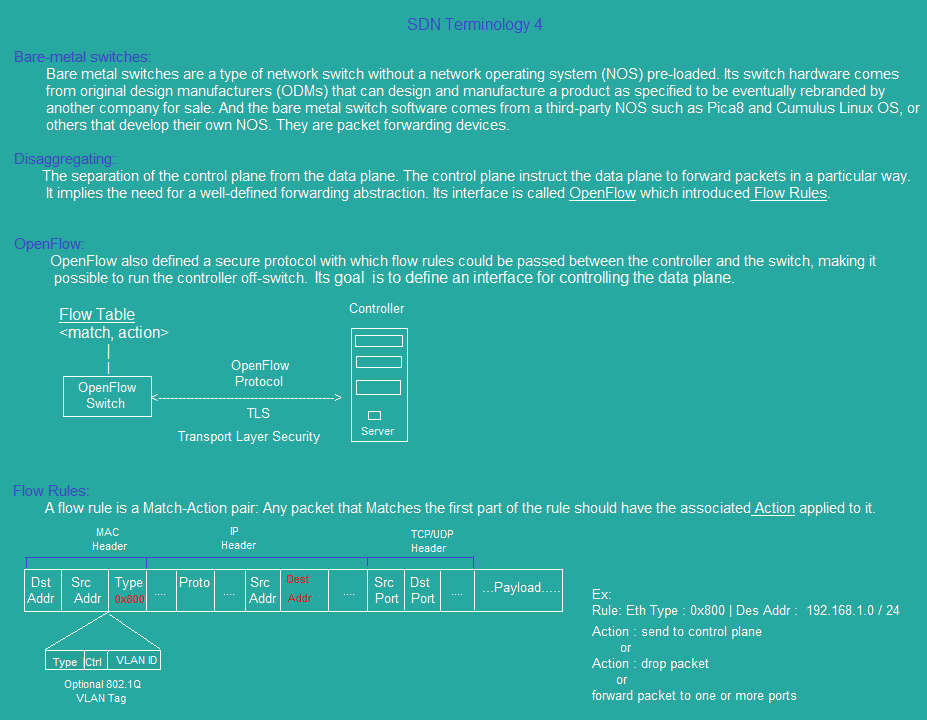

sdn_topology5
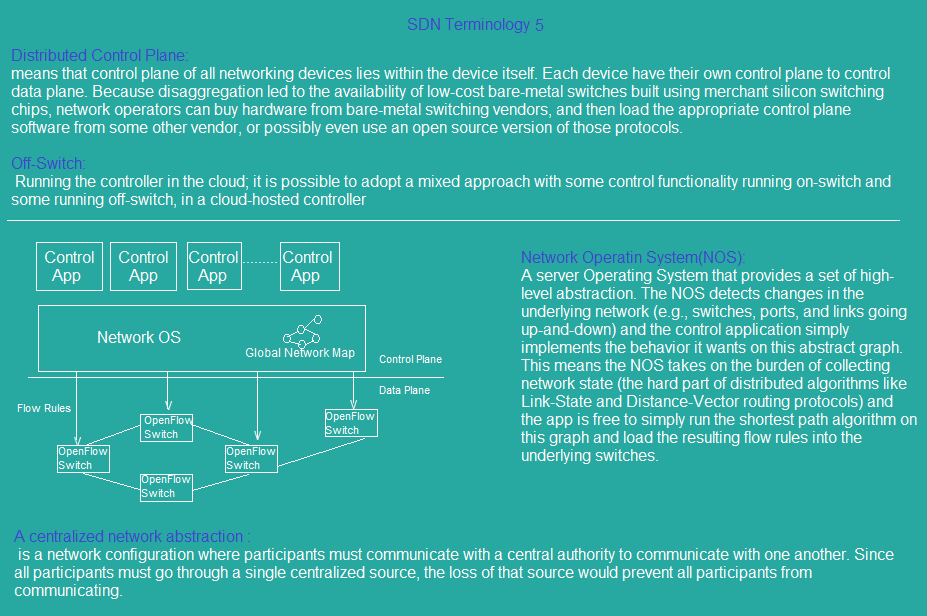

sdn_topology6


sdn_topology7


sdn_topology8
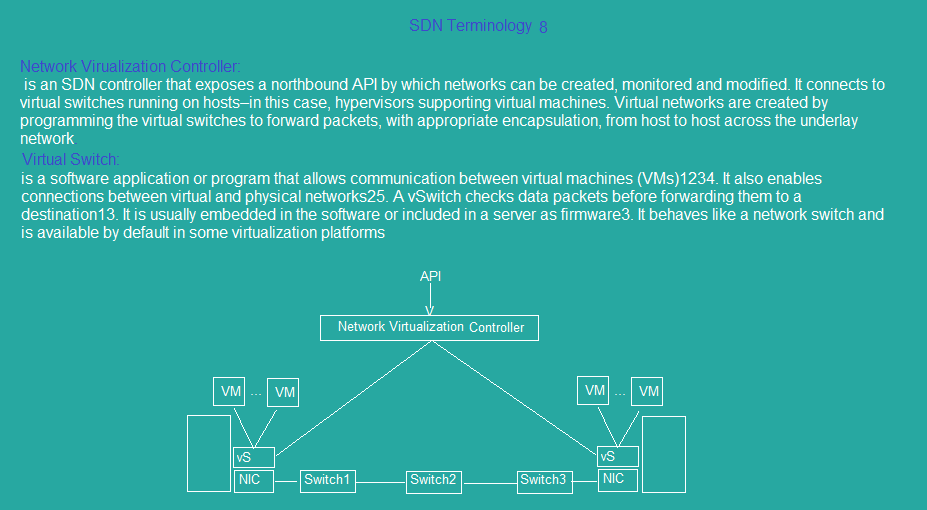

sdn_topology9


sdn_topology10
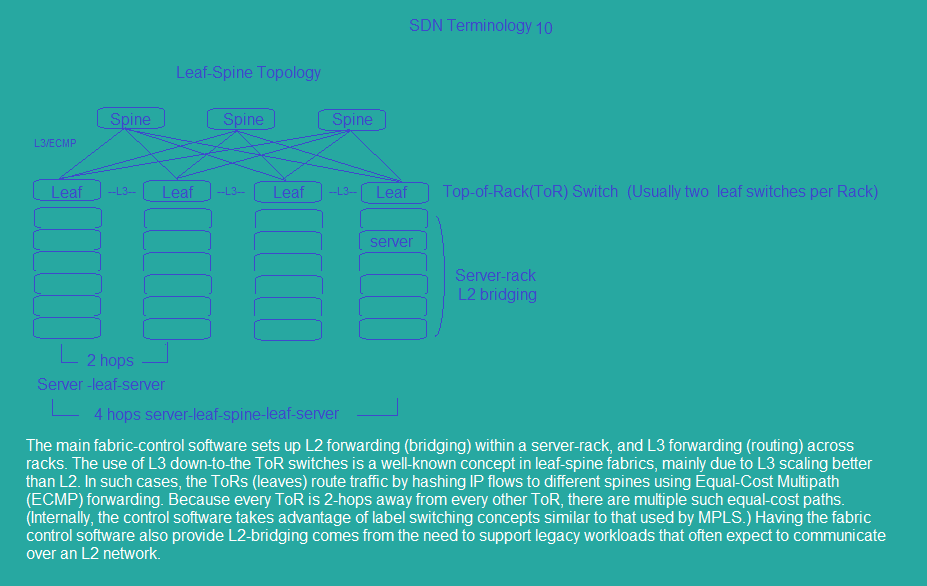

sdn_topology11


sdn_topology12
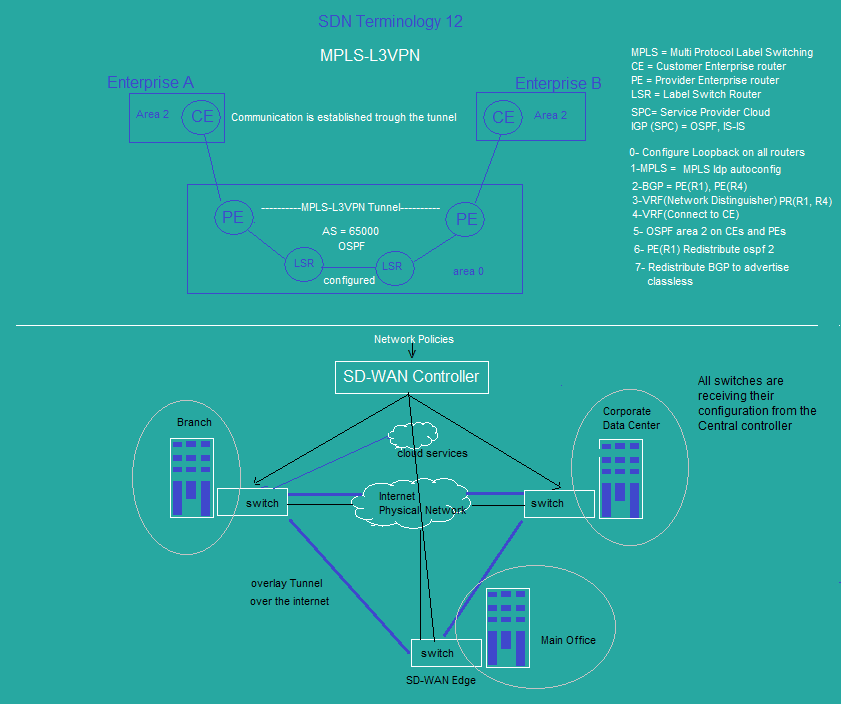

sdn_topology13


sdn_topology14


sdn_topology15
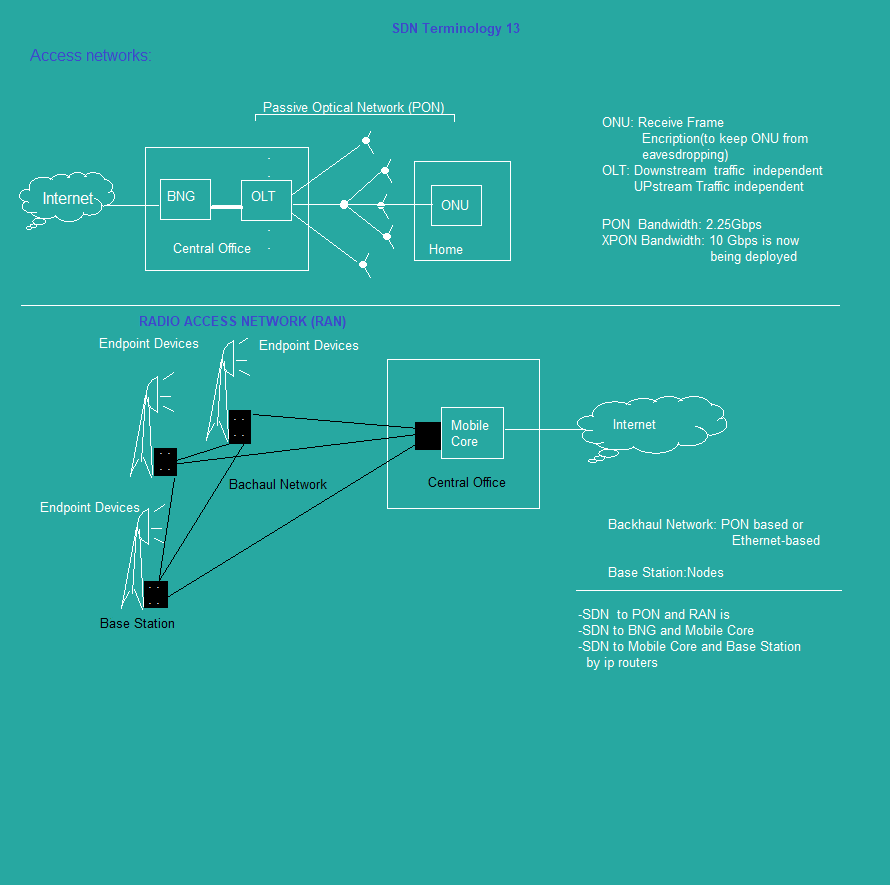

sdn_topology16


sdn_topology17


sdn_topology18


sdn_topology19


sdn_topology20


sdn_topology21


DATA |
data
![]()